iRAP has captured its first Decade of Action for Road Safety impact with an image-rich virtual story – “A World Free of High-Risk Roads: A Decade of Action to Save Lives”.
History
The Road Assessment Programme (RAP) and the New Car Assessment Programme (NCAP) were both founded by the British, Dutch and Swedish governments working in partnership with leading European automobile clubs and safety charities. Both the NCAP and RAP programmes have both been rolled out globally.
The European RAP programme was developed with funding from automobile clubs, national governments and a series of staged EU grants to create a “permanent institution”. The focus, like NCAP, was to create a market for safety by raising consumer awareness. By 2005, some 20 countries were applying or developing the safety ratings in Europe with programmes established in Australia, New Zealand and initiated in the USA that included both likelihood and severity outcomes.
2023
On November 7 2023 , the EuroRAP General Assembly took an historic step and unanimously voted for the dissolution of the EuroRAP entity. After 21 years of existence, the RAP programme in Europe is now being integrated into iRAP, the International Road Assessment Programme.
EuroRAP members have been instrumental in laying the foundation and inspiration for the Global Programme, which is now active in nearly 130 countries. Today, with this integration, RAP partners across Europe will benefit from having a streamlined administration and a more productive use of donor and partner resources.
iRAP will welcome expressions of interest from countries that may want to establish their own local ‘RAP’ (similar to BrazilRAP, AusRAP and United Kingdom RAP), to formalize coordination between organisations involved in road infrastructure safety: road agencies, institutes, and NGOs. ‘National License Agreements’ that are currently in place will formally come to a natural end in 2023.
The European Institute of Road Safety (EIRA), a not-for-profit entity established to support road safety projects in Europe, will continue in its role of helping countries make the most of the RAP methodologies, tools and resources.
2017
Thanks to all of our donors, partners and friends a lot has happened in the first 15 plus years of RAP and many lives have been saved. Join us to continue the innovation and expansion of impact as we seek to save lives and create a world free of high-risk roads in the years ahead.
2015
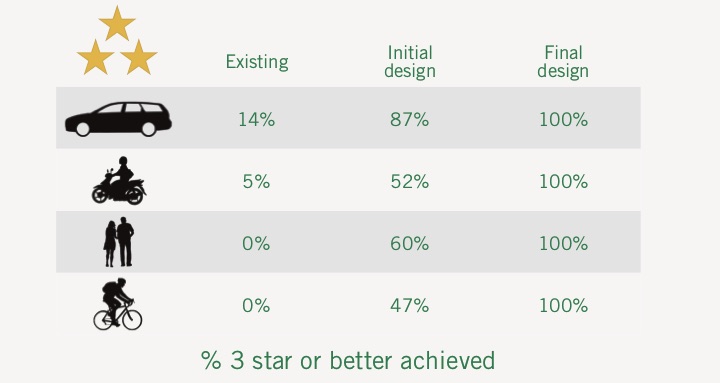
The independent 3-star coalition was formed by the Fund for Global Health and a wide range of partners from around the world combined to lend their support to the call for 3-star or better roads for all road users. Star Rating of Designs extended in application worldwide and the Qatar Government helped developed tools to make the process easier. FedEx has supported the further development of the Star Rating for Schools tablet app to ensure a free, simple and scalable solution for NGO's and school communities to apply globally.
Major governments launched dedicated safer roads funds including the impressive Highway Safety to Cherish Life programme in China, the Bruce and Midland Highway investment in Australia, the Safer Roads Alliance and Wellington Gateway projects in New Zealand, the Utah Government Strategic Highway Safety Plan, the Highways England and Department for Transport Safer Roads Fund in the UK as well as major development bank investment in low and middle-income countries.
2012
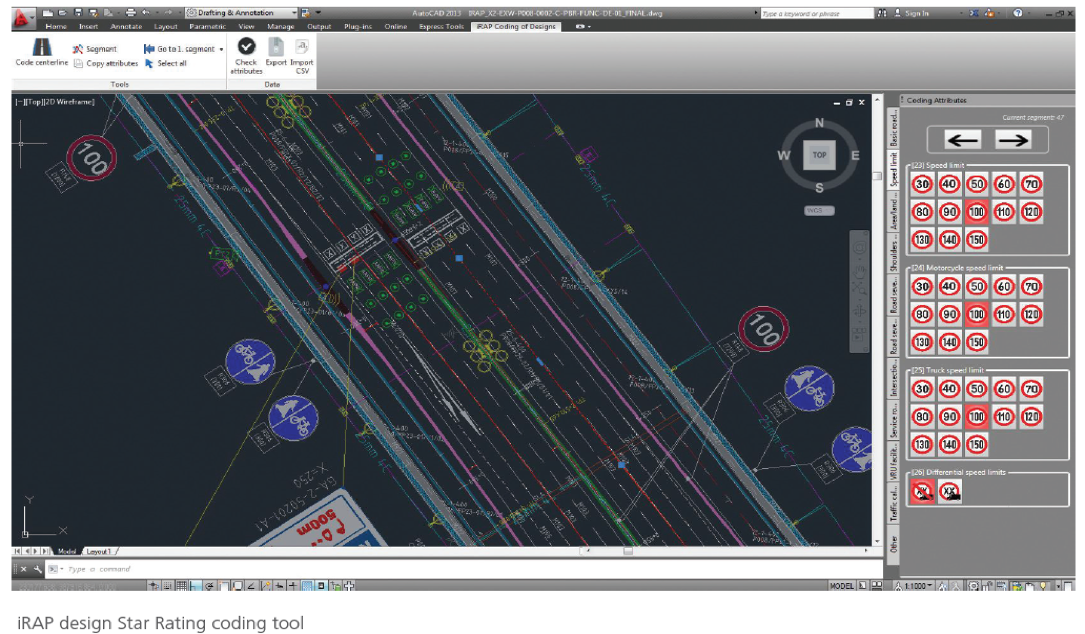
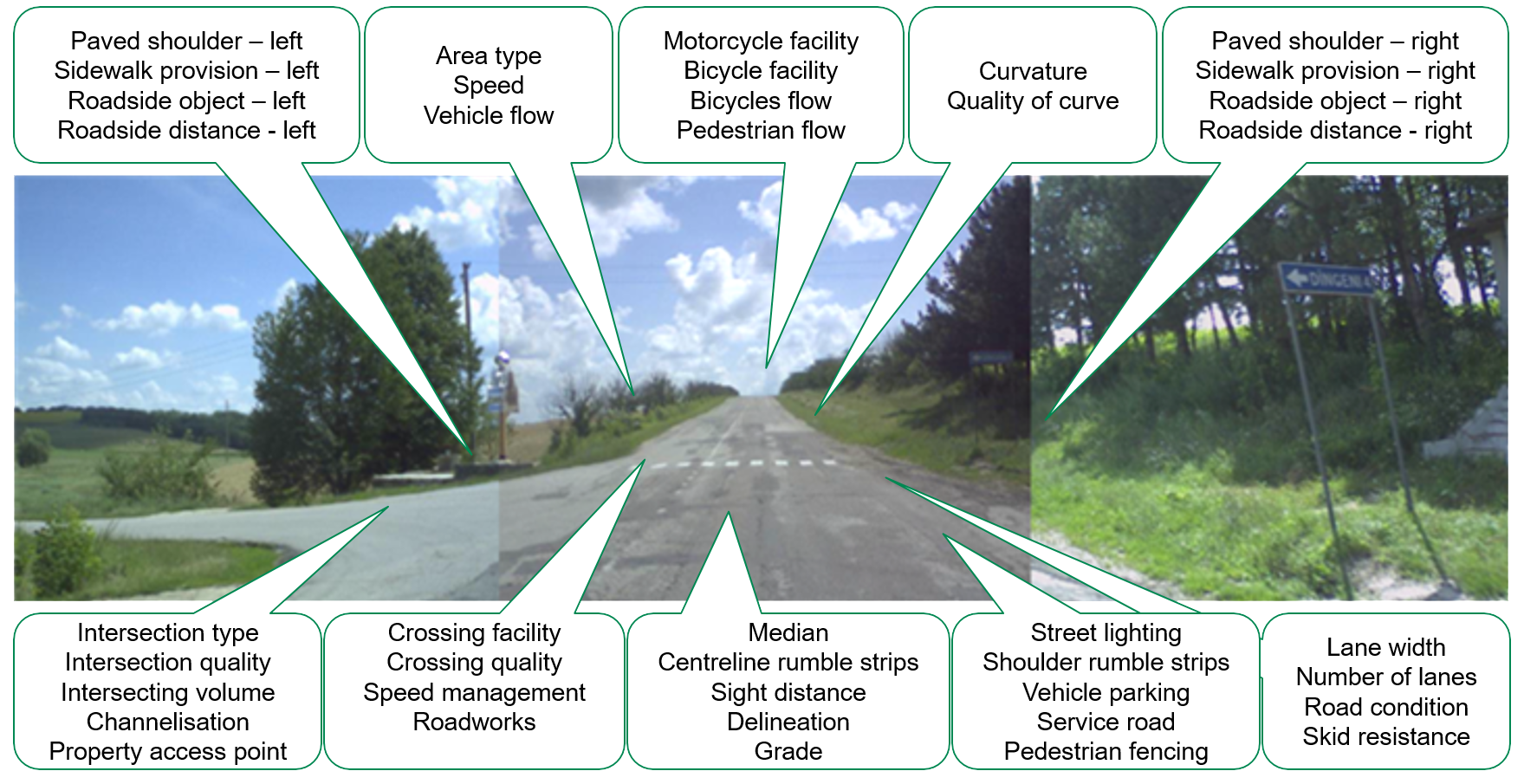
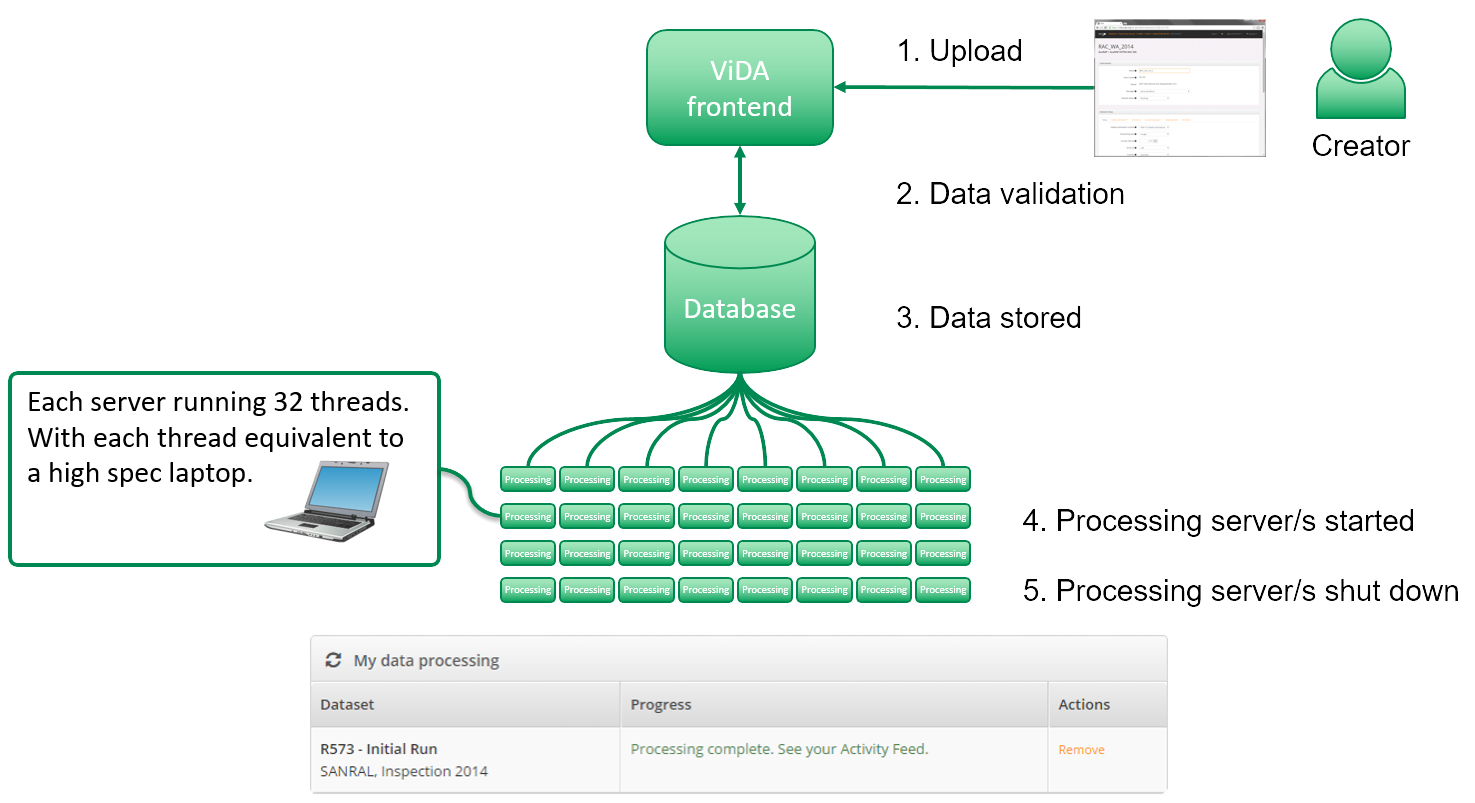
New software and systems were developed to support the scale of activity worldwide, overseen by the independent Global Technical Committee. Model innovation including urban risk mapping, star rating for schools and enhanced reporting for more advanced countries helped partners expand activity . Large scale application in urban and rural areas continued in countries like Mexico, India, China, Colombia, South Africa, Egypt, Australia, New Zealand, USA South East Europe. Major road lengths were now being upgraded based on iRAP recommendations.
2009
2006
iRAP was formed in 2006 and was granted charity status in 2011 (UK Registered Charity 1140257). The organisation forms the umbrella organization for road assessment programmes worldwide – e.g. Europe (EuroRAP), Australia (AusRAP), and the US (usRAP) and facilitates the development of road assessment work in low and middle income countries.
In 2006, following the suggestion of the World Bank, RAP techniques specifically tailored for use in low and middle income countries were developed using a €3m grant from the FIA Foundation. These were piloted in Chile, Costa Rica, Malaysia and South Africa.
2002
EuroRAP established as a Brussels-based International Non-Profit Association (AISBL) to manage Road Assessment Programmes across the EU. ADAC, ANWB and RSF – Founding Members.