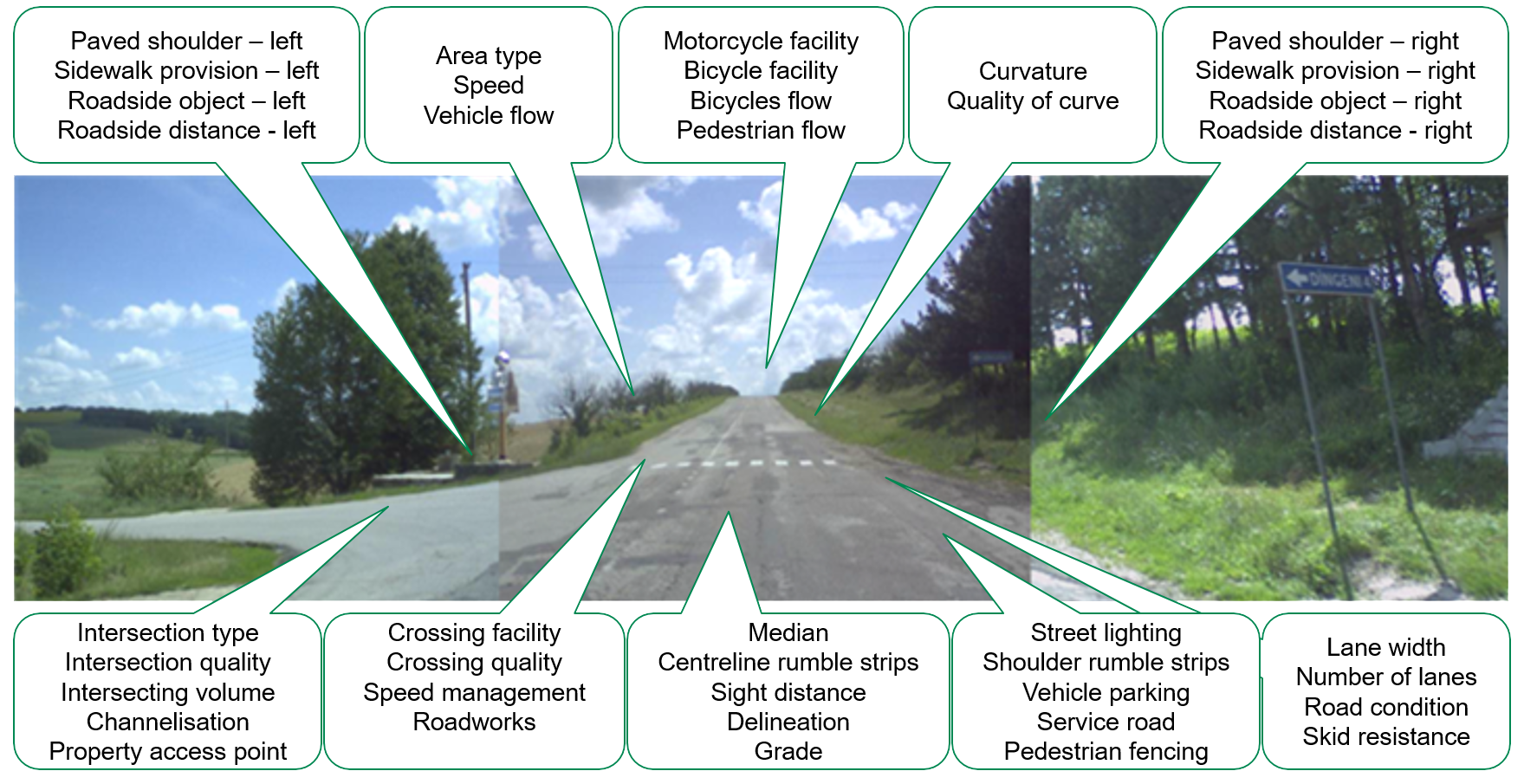
What is AiRAP?
Data is increasingly considered as critical to addressing the global road safety crisis. The UN Second Decade of Action aims to halve fatal and serious injury road crashes by 2030. For this to happen, the tools and methods used to assess and address high risk roads need to become integrated into every aspect of a road network’s planning, design, investment, construction, management and maintenance.
The AiRAP initiative was conceived by iRAP in 2019 to help improve access to, and application of, existing and emerging data sources globally, including advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, vision systems, LIDAR, telematics and other data sources. AiRAP stands for the ‘accelerated and intelligent’ capture of road safety-related data using automatic, repeatable and scalable methods to support road safety assessment, crash risk mapping, investment prioritisation for all road users.
iRAP’s new AiRAP accreditation ensures this data meets iRAP’s common global standard, which is already being used globally for recording of road features that impact road safety to streamline and benchmark performance.
How do I become an AiRAP data supplier?
iRAP has established a new AiRAP accreditation for the conversion of source data into iRAP attribute data. The AiRAP accreditation process will ensure data suppliers produce data in accordance with iRAP’s global standard format, regardless of the source of the data.
The accreditation process removes the need for complex data processing and storage for the data consumer. It also provides an understanding of the reliability of the data for different geographic regions, area types and road types, as well as when and how the data should be used. The process is flexible and accommodates data derived from different types of source data, as well as different collection and processing methods.
AiRAP news:
AiRAP R&D projects
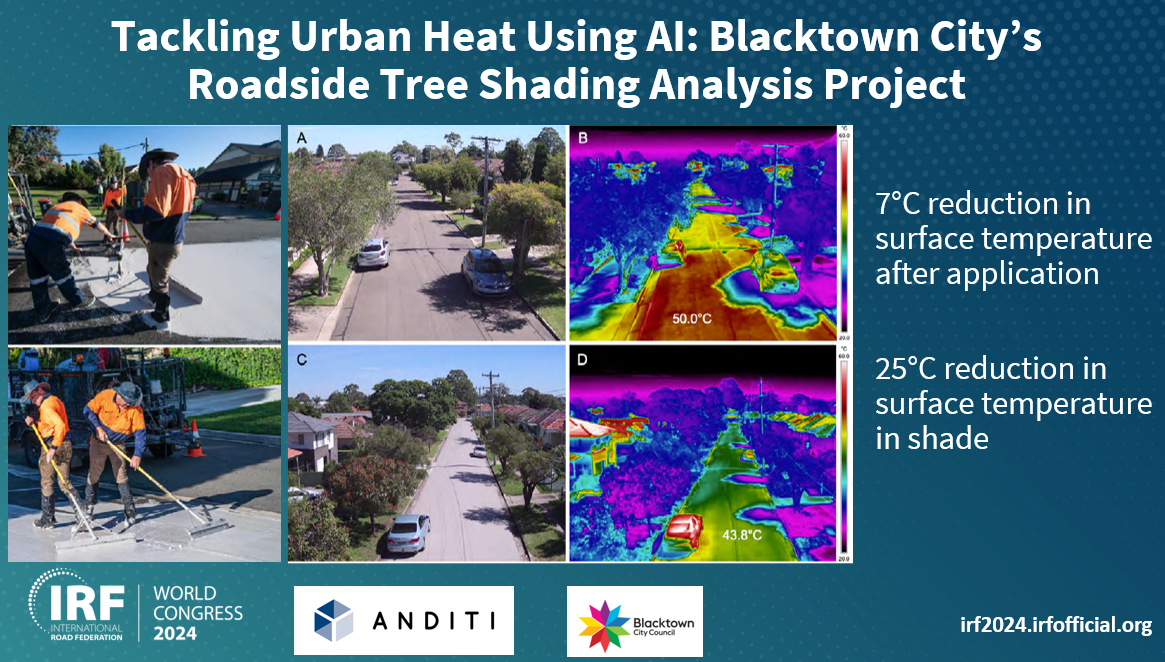
AiRAP is being piloted as part of a number of research and innovation projects globally.
The Leveraging Artificial Intelligence and Big Data to Enhance Safety Analysis research project will investigate the use of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML) and Big Data (BD) to improve the visibility of existing network conditions with a focus on road and exposure features influencing the safety of all road users across the entire road network.

The AiRAP Automation for Australian Road Safety project is funded by iMOVE CRC and supported by the Cooperative Research Centres program, an Australian Government initiative. The project will deliver 20,000 kilometres of road attribute data for the state road network in New South Wales using TomTom’s MN-R data, as well as prove feature extraction techniques and machine learning for LiDAR data.

The AI&Me: Leveraging AI Tools for Road Safety Impact Project, funded by Google.org, uses big data and artificial intelligence to map pedestrian risk across Vietnam and enhance road safety. By applying advanced AI models, the project identifies high-risk areas for pedestrians and optimizes Star Rating for Schools (SR4S) analyses, enabling faster, more accurate assessments and scalable interventions to improve safety for the schools’ communities.

The AI&Me Empowering Youth for Safer Roads project is funded by Fondation Botnar and supported by the FIA Foundation. The project is using big data and AI to map pedestrian risk around 1,000 schools in Vietnam and develop an app to connect young voices with decision-makers for safer roads.

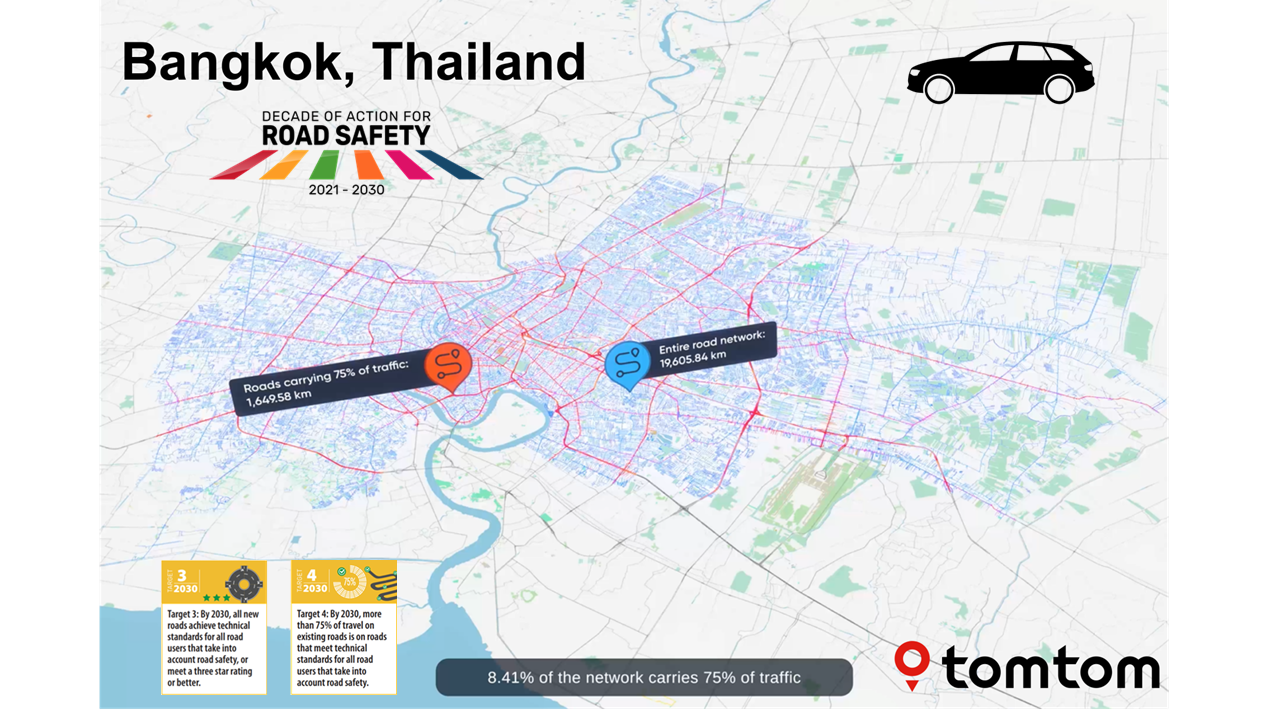
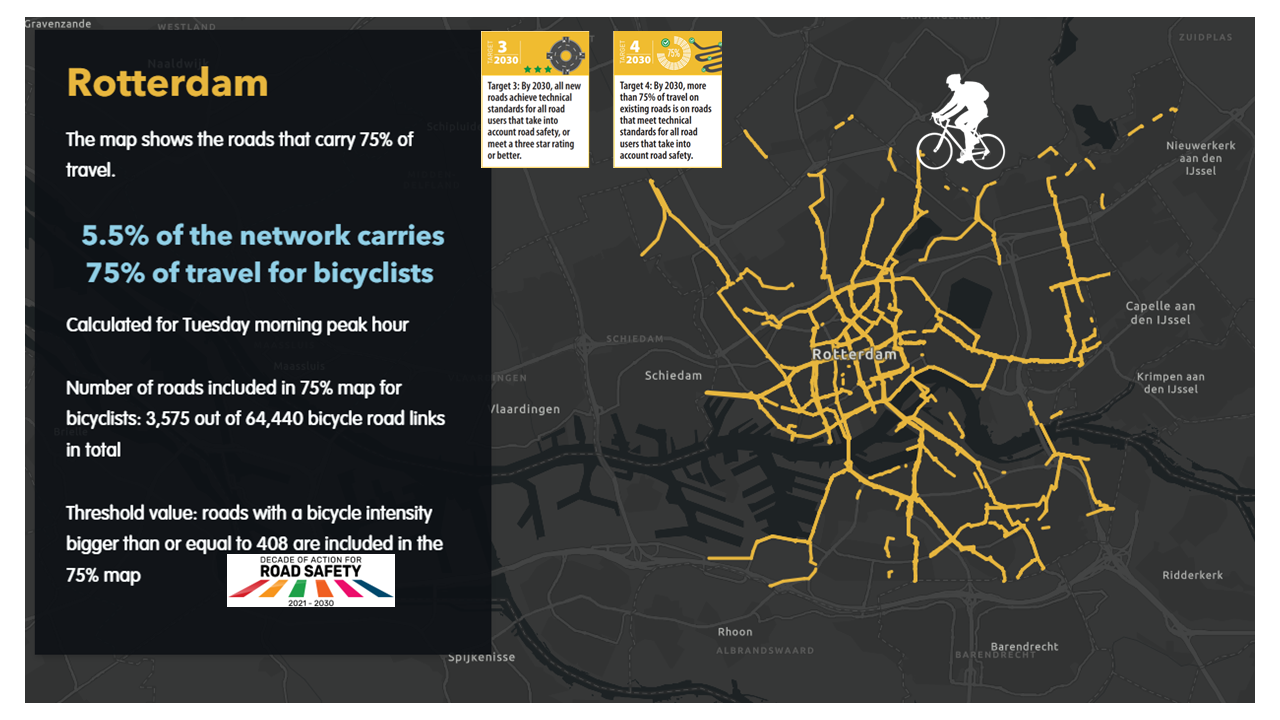
The Regional Road Safety Observatories (RRSOs) Road Safety data collection in LMICs project is funded by the World Bank. The project piloted the use of satellite data, amongst others, to map where 75% of travel occurs across two countries, Kenya and Ethiopia, and trialed the detection of speed, flow and other physical road features for the measuring and monitoring of road safety key performance indicators (KPIs).

In partnership iRAP, the IDB has developed VíaSegura, a digital initiative to assess road infrastructure safety. The tool focuses on evaluating a set of variables used in the Star Rating methodology.

In early 2021, more than 30 machine learning engineers, subject matter experts, and mentors collaborated as part of an Omdena challenge to work towards iRAP’s vision of “a world free of high-risk roads. The project, titled Using Convolutional Neural Networks To Improve Road Safety And Save Lives, built AI based solutions to increase road safety by mapping the crash risk on roads.
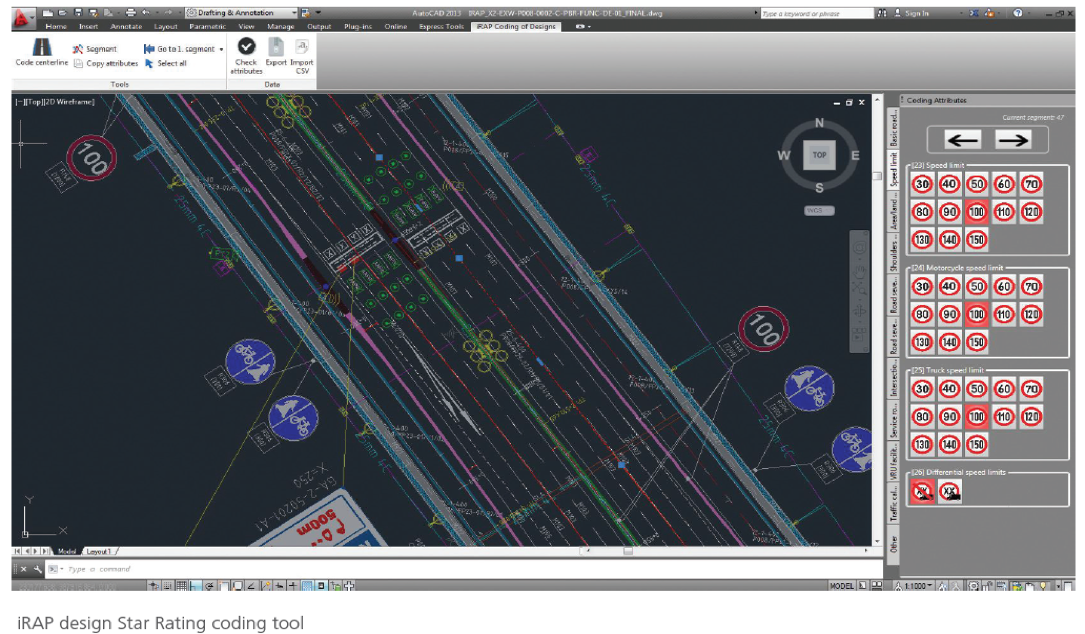
The European Commission CEF funded project SLAIN (Saving Lives Assessing and Improving TEN-T road Network safety) aims to extend the skills and knowledge base of partners in performing network-wide road assessment. Deliverables 7.3 and 7.4 relate to the methodology and improvement of automatic road-attribute coding for network-wide assessments.

For more information
Please contact:
Monica Olyslagers
Global Innovation Manager and Cities Specialist
monica.olyslagers@irap.org
Andrejus Laugman
Technical Development Manager
andrejus.laugman@irap.org