iRAP was proud to present this week, alongside UN Special Envoy for Road Safety Jean Todt, global AI innovators and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) at the Fourth Global Standards Symposium (GSS) calling for technical standards to support progress towards global socio-economic and environmental goals.
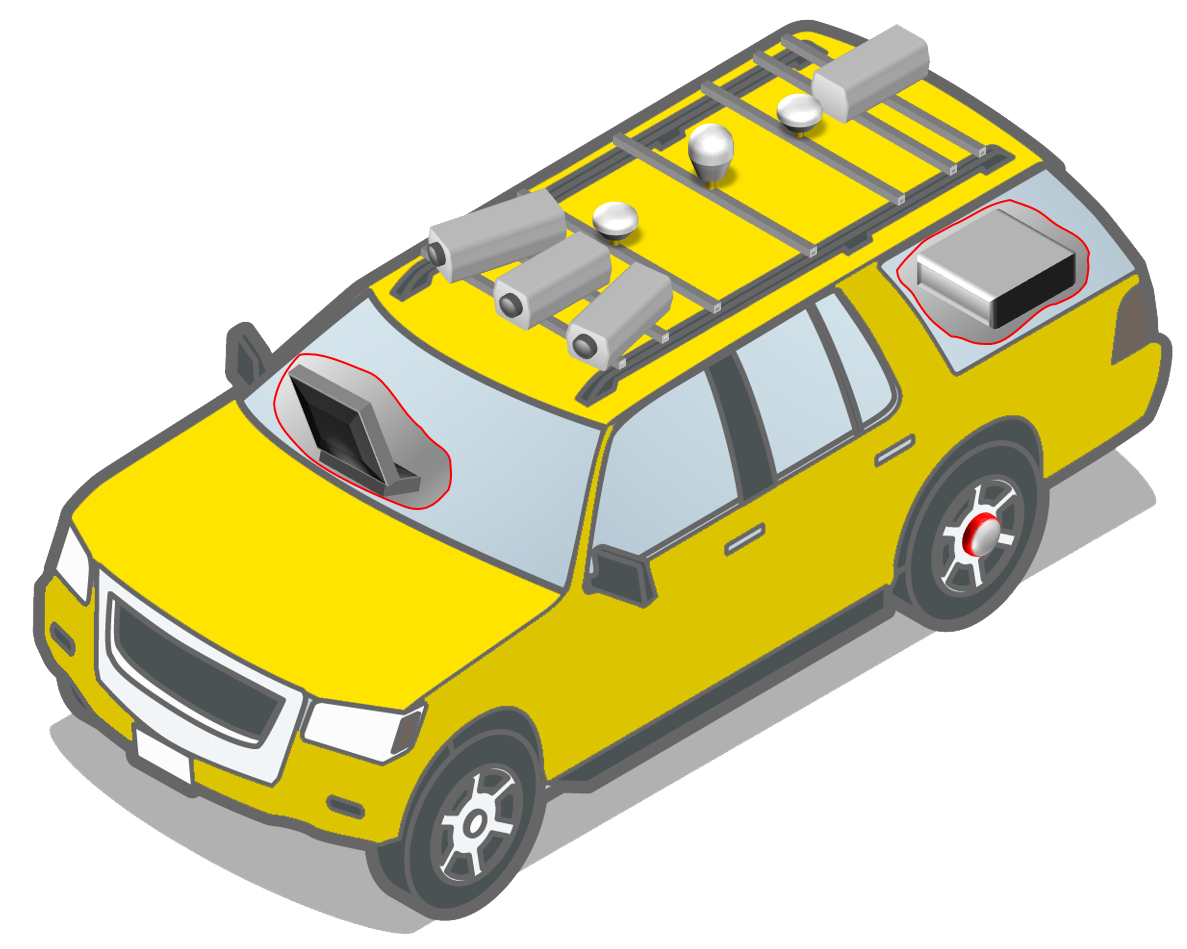
iRAP Product Director James Bradford presented on the AiRAP Initiative which aims for the accelerated and intelligent capture of road safety assessment data to the global standard. AiRAP will utilise advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, vision systems, LIDAR, telematics and other data sources to deliver critical information on road safety, crash performance, investment prioritisation for all road users.
Digital leaders recognize that technical standards, built through patient, continuous collaboration, are key foundations to harness emerging technologies for the good of everyone on the planet.
“Digital technologies provide opportunities but also risks, including risks to the international order – that is under stress and that we can guarantee only by working together,” said H.E. Nele Leosk, GSS-20 Chairman and Estonia’s Ambassador-at-Large for Digital Affairs.
GSS-20 – delayed two years by the COVID-19 pandemic – submitted its conclusions to the World Telecommunication Standardization Assembly (WTSA) now underway in Geneva, Switzerland.
ITU membership discussions at WTSA between 1 and 9 March will review the strategic direction of ITU work on standards to meet emerging industry and societal needs.
How tech can serve sustainable development
The one-day symposium underlined eight key priorities for the global standardization community:
- Cooperate on standards for sustainable digital transformation
The world’s leading developers of international standards – ITU, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) – along with numerous other standards bodies, should keep collaborating to facilitate digital transformation and bridge standardization gaps between developed and developing countries.
- Unlock the full potential of digital transformation for sustainable development
Countries and companies will need clear technological and digitalization guidance to engage in effective climate action, cutting their emissions in line with the Glasgow Climate Pact and the Paris Agreement, along with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set out by the United Nations for 2030.
As part of this, the symposium’s conclusions called for ITU, ISO and IEC to contribute actively to the world’s energy transition, provide a decarbonization pathway for the ICT (information and communication technology) sector, support initiatives for net-zero emissions by 2050, and develop clear standards to measure progress towards net-zero commitments.
- Foster cross-sectoral innovation for people-oriented cities and communities
United for Smart Sustainable Cities (U4SSC), an ongoing initiative supported by ITU the UN Economic Commission for Europe, UN Habitat, and another 14 UN partners provides expert guidance for digital transformation at the city level and drives collaboration that has led more than 150 cities to adopt U4SSC Key Performance Indicators based on ITU standards.
- Make the world’s ongoing digital transformation sustainable
Technical standardization that promotes sustainability, circularity, and resilience will help accelerate the transition to a net-zero, energy-efficient and ultimately circular, waste-free economy.
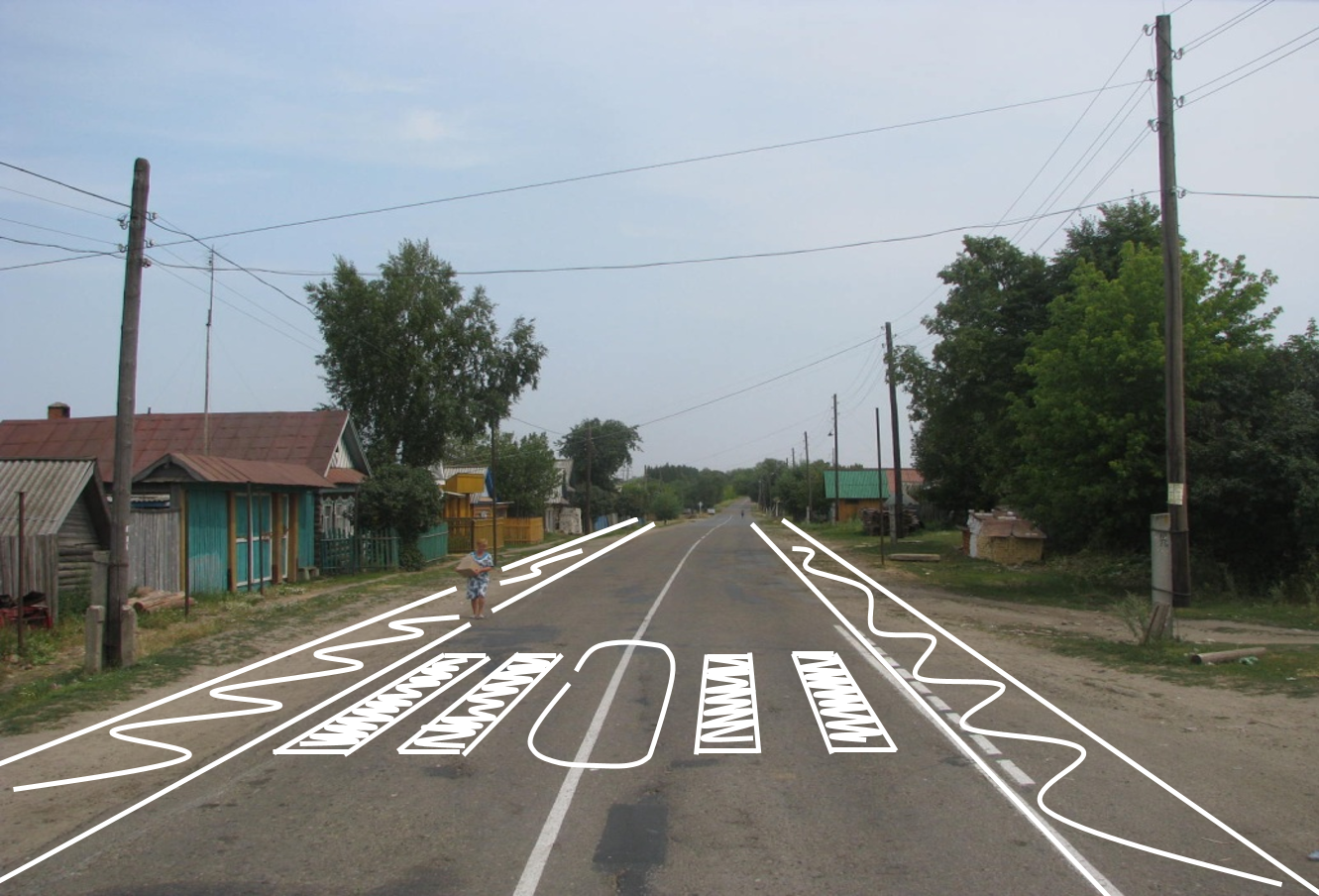
- Promote artificial intelligence (AI) for road safety
Connectivity plays a decisive and important role in enabling assisted and automated driving and ensuring road safety for all.
- Leverage digital health technologies for equitable healthcare access
Digital health systems can fundamentally transform healthcare services for the elderly, the poor, and people in rural communities, empowering patients, enabling healthcare providers to deliver better care, and improving treatments for everyone, especially during global health emergencies.
- Boost financial inclusion for all
Technical standards can help lower ICT costs, enhance the resilience of digital infrastructure, and support high levels of security for financial transactions, in line with the outcomes of the Financial Inclusion Global Initiative by ITU, the World Bank and the Committee on Payments and Market Infrastructures (CPMI), with the support of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Strengthen standards to overcome challenges, maximize opportunities, accelerate digital transformation, and achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals
Developing countries face challenges in implementing standards and frameworks to accelerate digital transformation – a constraint addressed by an ITU programme, Bridging the Standardization Gap.
Maintaining technical cooperation
Participants in the 28 February symposium exchanged views on the priorities for ITU’s standardization arm during the coming 2022-2024 study period.
Ambassador Leosk, the first woman holding the GSS chair, stressed the need always to press on with technical standardization. “Let us keep forging a future that is more free, sustainable, inclusive and peaceful,” she said.
Download the Global Standards Symposium conclusions.
Read more on AiRAP and plans for the future here.