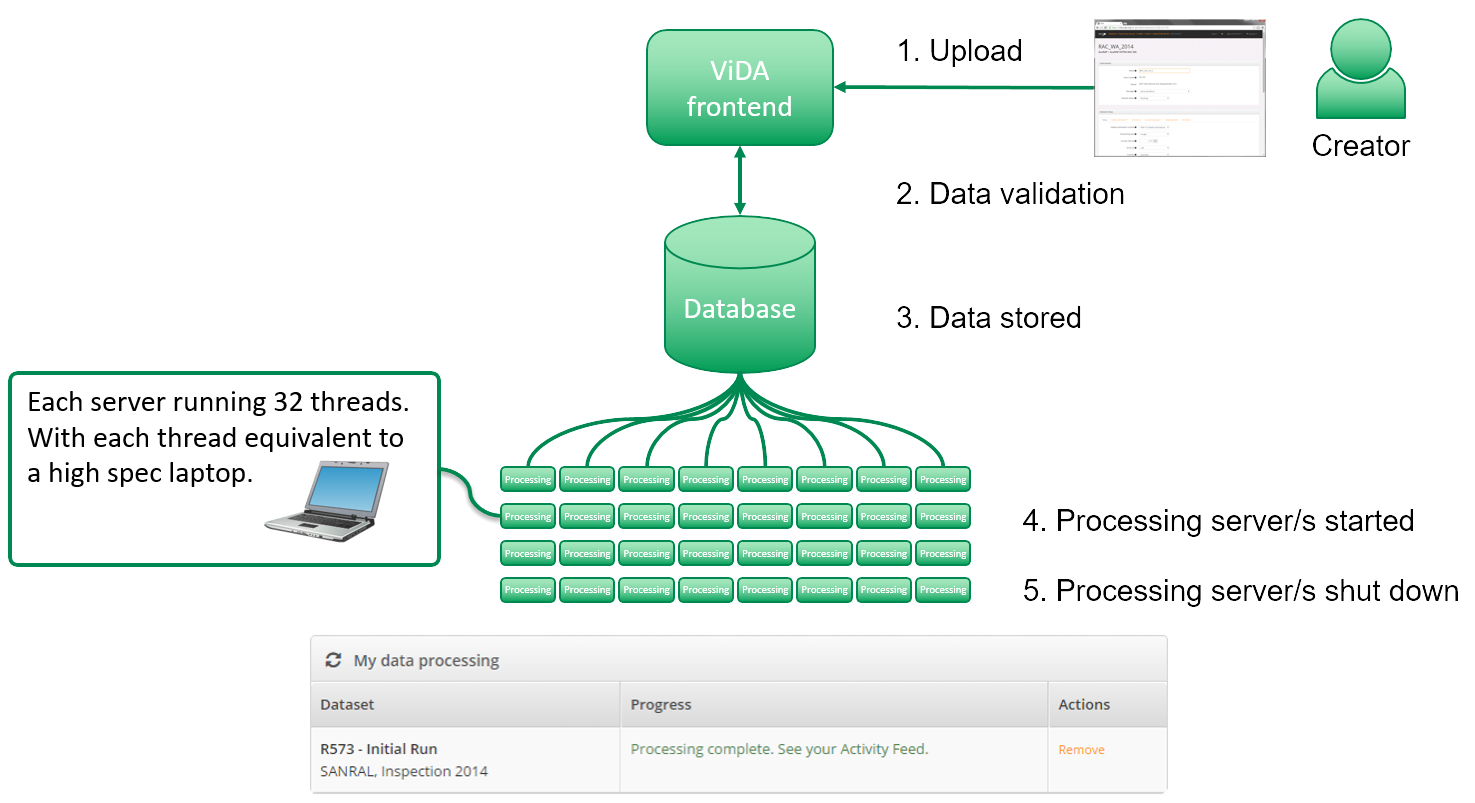
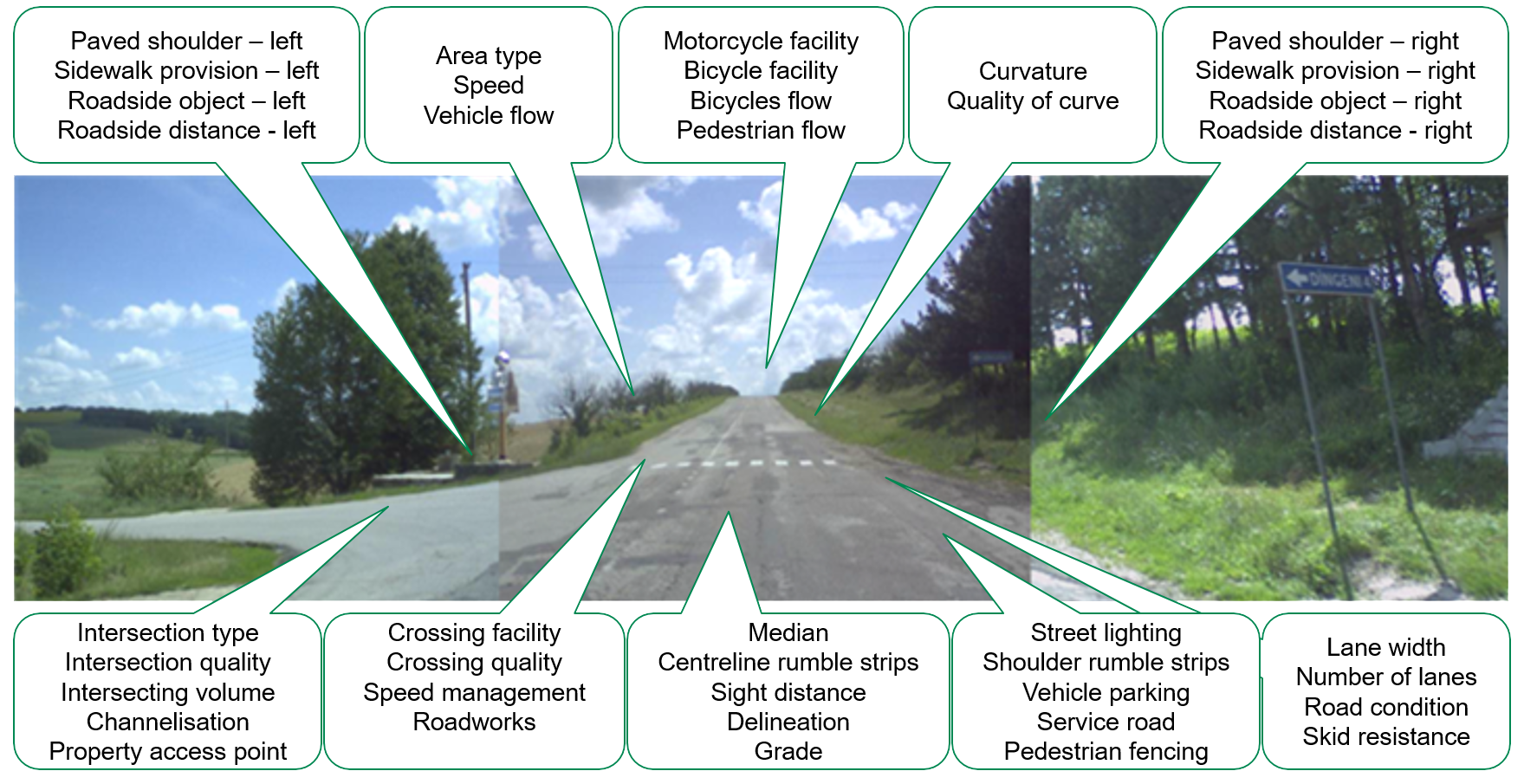
How RAP tools and resources can support RISM
There are several ways in which RAP tools and resources may be used to support the implementation of RISM. The SLAIN project, for example, showed how reactive Risk Mapping can be used to guide selective Star Ratings in order to prioritize a safety response.
The following table summarises how RAP tools and resources may be used to support specific articles of RISM.
| RISM Directive Article/Paragraph | Description | iRAP tools and resources |
| Art. 5 | Network-wide road safety assessment | |
| 5/2 | Ability to evaluate accident and impact severity risk | Star Ratings and Risk Mapping may be used at the network level. A tool is under development to convert Star Ratings into NWRSA outputs. |
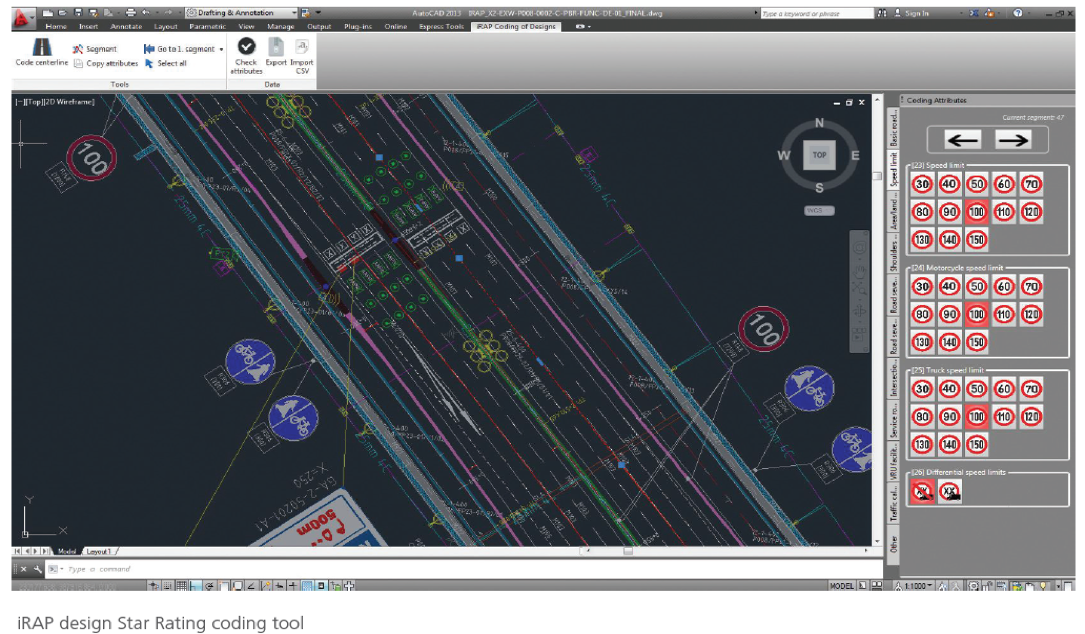
| 5/2a | Involves visual examination, either on site or by electronic means, of the design characteristics of the road (in-built safety) | RAP Star Ratings involve visual assessment of the level of safety that is ‘built-in’ to roads. |
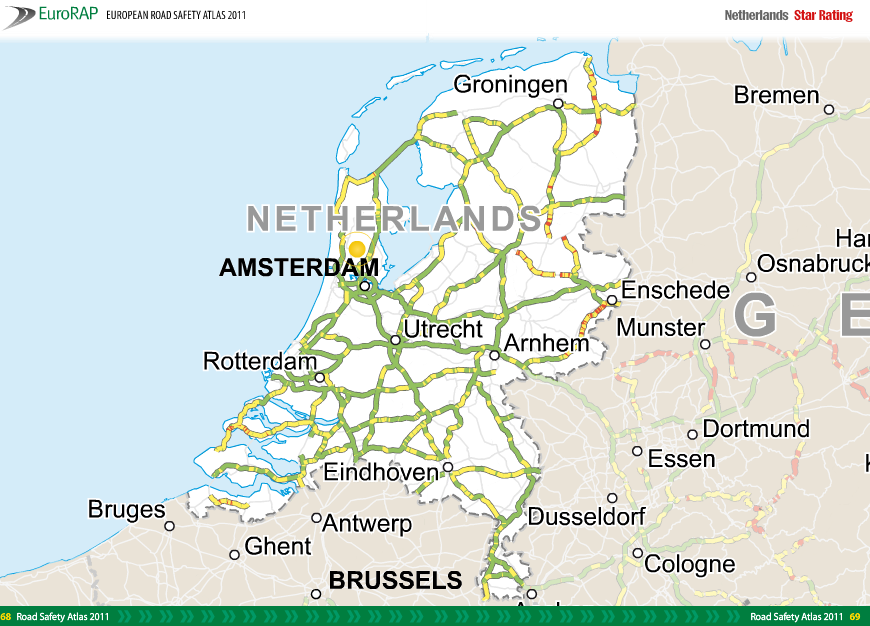
| 5/3 | Repeatability – enables periodic inspections and comparability of results | Star Ratings and Risk Mapping use a standardised methodologies that are used to track performance over time |
| 5/6 | Classification of all sections of the road network in no fewer than three categories according to their level of safety | Star Ratings and RIsk Mapping involves categorising road segments into one of 5 risk categories. |
| Art. 6 | Periodic road safety inspections | |
| 6/1 | Periodic road safety inspections are undertaken with sufficient frequency to safeguard adequate safety levels for the road infrastructure in question | Star Ratings and Risk Mapping may be performed periodically as part of performance tracking |
| Art. 6a | Follow-up of procedures for roads in operation | |
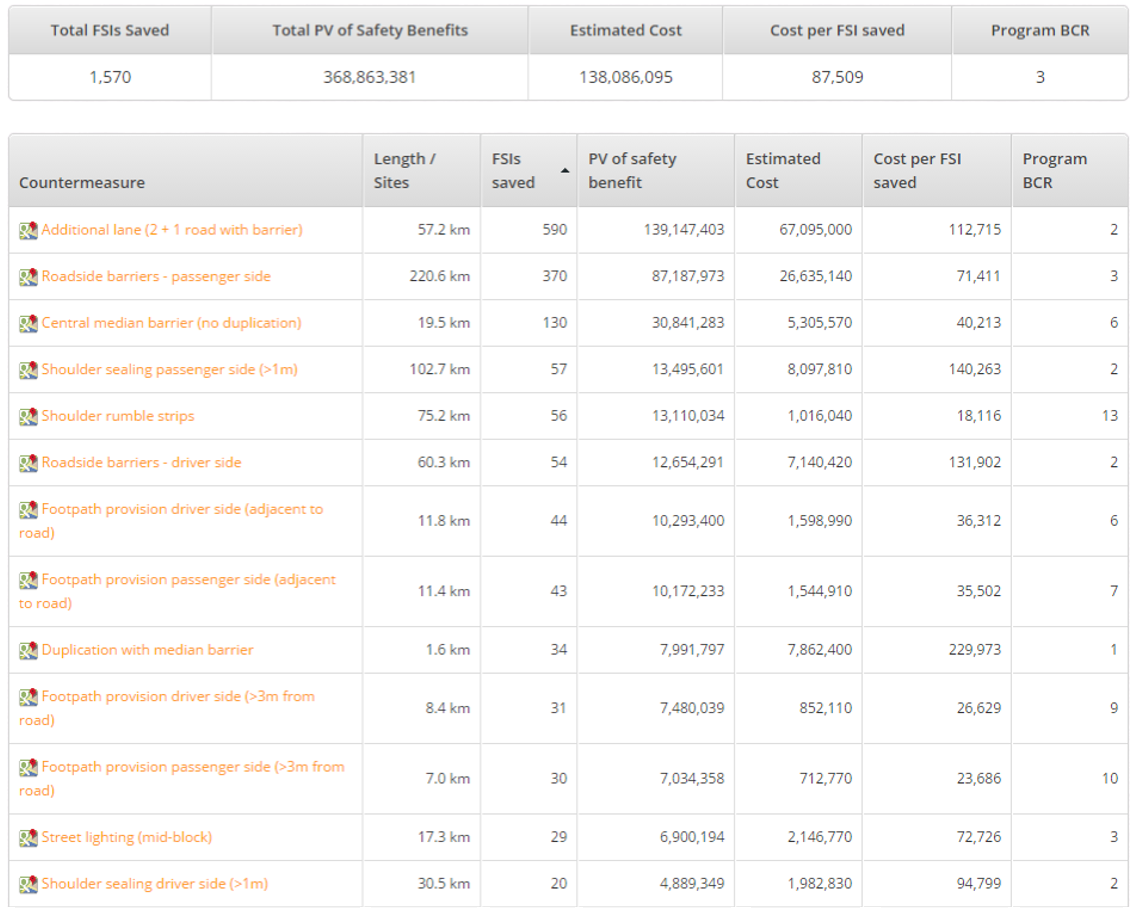
| 6a/1 | Network-wide road safety assessments are followed up either by targeted road safety inspections or by direct remedial action | Fatality and Serious Injury (FSI) estimates and Safer Road Investment Plans (SRIP) may be used to assist in identifying and implementing priority countermeasures on priority road segments |
| 6a/2 | Indicative elements (Annex IIa) for targeted road safety inspections. | See table below |
| 6a/3 | Targeted road safety inspections shall be carried out by expert teams | RAP tools and resources are supported by Training and a network of Accredited suppliers and practitioners |
| 6a/4 |
Findings of targeted road safety inspections are followed up by reasoned decisions determining if remedial action is necessary, and Identification of road sections where road infrastructure safety improvements are necessary and define actions to be prioritised for improving the safety of those road sections |
Fatality and Serious Injury (FSI) estimates and Safer Road Investment Plans (SRIP) may be used to assist in identifying and implementing priority countermeasures on priority road segments |
| 6a/5 |
Ensure remedial action is targeted primarily at road sections with low safety levels, and Which offer the opportunity for the implementation of measures with high potential for safety development and accident cost savings. |
Fatality and Serious Injury (FSI) estimates and Safer Road Investment Plans (SRIP) may be used to assist in identifying and implementing priority countermeasures on priority road segments |
| 6a/6 | Prepare and regularly update a risk-based prioritised action plan to track the implementation of identified remedial action. | RAP assessments may be performed at periodic intervals |
| Art. 6b | Protection of vulnerable road users | |
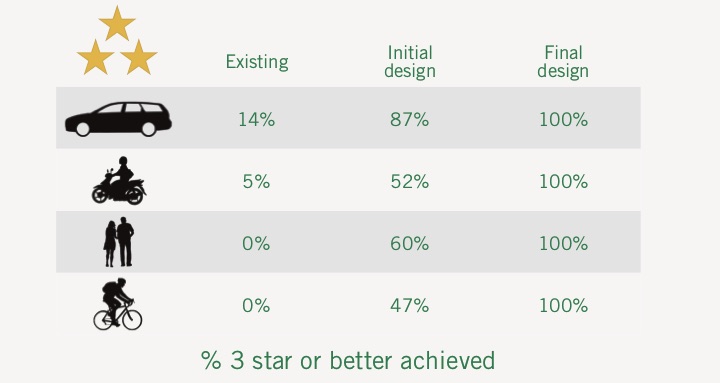
| 6b | Needs of vulnerable road users are taken into account in the implementation of the procedures set out in Articles 3 to 6a. | Star Ratings, FSI estimations, SRIPs and Risk Mapping account for vulnerable road users, including pedestrians, bicyclists and motorcyclists. |
Using Star Rating to satisfy requirements of the Network-Wide Road Safety Assessments
iRAP’s Star Rating methodology covers most of the indicative elements of network-wide road safety assessment as listed in Annex III. The table below provides more details.
| RISM recommended elements | Alignment with Star Rating methodology |
| 1. General: | |
| (a) type of road in relation to the type and size of regions/cities it connects; | Partially or not directly covered, but collected for assessment purpose and can be extrapolated from available data |
| (b) length of road section; | ✔ |
| (c) area type (rural, urban); | ✔ |
| (d) land use (educational, commercial, industrial and manufacturing, residential, farming and agricultural, undeveloped areas); | ✔ |
| (e) property access points density; | Partially or not directly covered, but collected for assessment purpose and can be extrapolated from available data |
| (f) presence of service road (e.g. for shops); | ✔ |
| (g) presence of road works; | ✔ |
| (h) presence of parking. | ✔ |
| 2. Traffic volumes: | |
| (a) traffic volumes; | ✔ |
| (b) observed motorcycle volumes; | ✔ |
| (c) observed pedestrian volumes on both sides, noting ‘along’ or ‘crossing’; | ✔ |
| (d) observed bicycle volumes on both sides, noting ‘along’ or ‘crossing’; | ✔ |
| (e) observed heavy vehicle volumes; | ✔ |
| (f) estimated pedestrian flows determined from adjacent land use attributes; | ✔ |
| (g) estimated bicycle flows determined from adjacent land use attributes. | ✔ |
| 3. Accident data: | |
| (a) number, location and cause of fatalities by road user group; | Partially or not directly covered, but collected for assessment purpose and can be extrapolated from available data |
| (b) number and location of serious injuries by road user group. | Partially or not directly covered, but collected for assessment purpose and can be extrapolated from available data |
| 4. Operational characteristics: | |
| (a) speed limit (general, for motorcycles; for trucks); | ✔ |
| (b) operating speed (85th percentile); | ✔ |
| (c) speed management and/or traffic calming; | ✔ |
| (d) presence of ITS devices: queue alerts, variable message signs | – |
| (e) school zone warning; | ✔ |
| (f) presence of school crossing supervisor at prescribed periods. | ✔ |
| 5. Geometric characteristics: | |
| (a) cross section characteristics (number, type and width of lanes, central median shoulders layout and material, cycle tracks, foot paths, etc.), including their variability; | ✔ |
| (b) horizontal curvature; | ✔ |
| (c) grade and vertical alignment; | ✔ |
| (d) visibility and sight distances. | ✔ |
| 6. Objects, clear zones and road restraint systems: | |
| (a) roadside environment and clear zones; | ✔ |
| (b) fixed obstacles at the roadside (e.g. lighting poles, trees, etc.); | ✔ |
| (c) distance of obstacles from roadside; | ✔ |
| (d) density of obstacles; | Partially or not directly covered, but collected for assessment purpose and can be extrapolated from available data |
| (e) rumble strips; | ✔ |
| (f) road restraint systems. | ✔ |
| 7. Bridges and tunnels: | |
| (a) presence and number of bridges, as well as relevant information concerning them; | – |
| (b) presence and number of tunnels, as well as relevant information concerning them; | – |
| (c) visual elements representing hazards for the safety of the infrastructure. | – |
| 8. Intersections: | |
| (a) intersection type and number of arms (noting in particular the type of control and the presence of protected turns); | ✔ |
| (b) presence of channelisation; | ✔ |
| (c) intersection quality; | ✔ |
| (d) intersecting road volume; | ✔ |
| (e) presence of level crossings (noting, in particular, the type of crossing and whether they are manned, unmanned, manual or automated). | Partially or not directly covered, but collected for assessment purpose and can be extrapolated from available data |
| 9. Maintenance: | |
| (a) pavement defects; | ✔ |
| (b) pavement skid resistance; | ✔ |
| (c) shoulder condition (including vegetation); | ✔ |
| (d) condition of signs, markings and delineation; | ✔ |
| (e) condition of road restraint systems. | – |
| 10. Vulnerable road users’ facilities: | |
| (a) pedestrian and cycling crossings (surface crossings and grade separation); | ✔ |
| (b) cycling crossings (surface crossings and grade separation); | ✔ |
| (c) pedestrian fencing; | ✔ |
| (d) existence of sidewalk or separated facility; | ✔ |
| (e) bicycle facilities and their type (cycle paths, cycle lanes, other); | ✔ |
| (f) quality of pedestrian crossings with regard to the conspicuity and sign posting of each facility; | ✔ |
| (g) pedestrian and cycling crossing facilities on entry arm of minor road joining network; | ✔ |
| (h) existence of alternative routes for pedestrians and cyclists where there are no separated facilities. | – |
| 11. Pre/post-crash systems for traffic injury and gravity mitigation elements: | |
| (a) network operational centres and other patrolling facilities; | – |
| (b) mechanisms to inform road users of driving conditions in order to prevent accidents or incidents; | – |
| (c) AID (automatic incident detection) systems: sensors and cameras; | – |
| (d) incident management systems; | – |
| (e) systems for communicating with emergency services. | – |
| (d) condition of signs, markings and delineation; | – |
| (e) condition of road restraint systems. | – |
Using Star Ratings to support targeted Road Safety Inspections
The following table summarises how the RAP Star Rating methodology aligns with indicative elements of targeted road safety inspections listed in RISM Annex IIa.
| RISM recommended elements | Alignment with Star Rating methodology |
| 1. Road alignment and cross-section: | |
| (a) visibility and sight distances; | ✔ |
| (b) speed limit and speed zoning; | ✔ |
| (c) self-explaining alignment (i.e. “readability” of the alignment by road users); | Partial – uses sight distance, curvature, grade and delineation to indicate readability |
| (d) access to adjacent property and developments; | ✔ |
| (e) access of emergency and service vehicles; | Partial – Can be derived from paved shoulder width data |
| (f) treatments at bridges and culverts; | ✔ |
| (g) roadside layout (shoulders, pavement drop-off, cut and fill slopes). | ✔ |
| 2. Intersections and interchanges: | |
| (a) appropriateness of intersection/interchange type; | |
| (b) geometry of intersection/interchange layout; | Partial – provides for how many legs of an intersection (up to 4), but does not take into account angles |
| (c) visibility and readability (perception) of intersections; | Partial – uses sight distance, curvature, grade, delineation and intersection quality |
| (d) visibility at the intersection; | Partial – uses sight distance, curvature, grade, delineation and intersection quality |
| (e) layout of auxiliary lanes at intersections; | Partial – indicates if turning lanes are present or not for inspected road |
| (f) intersection traffic control (e.g. stop controlled, traffic signals, etc.); | ✔ |
| (g) existence of pedestrian and cycling crossings. | ✔ |
| 3. Provision for vulnerable road users: | |
| (a) provision for pedestrians; | ✔ |
| (b) provision for cyclists; | ✔ |
| (c) provision for powered-two-wheelers; | ✔ |
| (d) public transport and infrastructures; | – |
| (e) level crossings (noting, particularly, the type of crossing and if they are manned, unmanned, manual, or automated). | ✔ |
| 4. Lighting, signs and markings: | |
| (a) coherent road signs, not obscuring visibility; | Partial – recorded as part of delineation and sight distance |
| (b) readability of road signs (position, size, colour); | Partial – recorded as part of delineation |
| (c) sign posts; | Partial – recorded as part of delineation |
| (d) coherent road markings and delineation; | ✔ |
| (e) readability of road markings (position, dimensions and retroreflectivity under dry and wet conditions); | Partial – recorded as part of delineation |
| (f) appropriate contrast of road markings; | Partial – recorded as part of delineation |
| (g) lighting of lit roads and intersections; | Partial – presence of street lighting recorded |
| (h) appropriate roadside equipment. | |
| 5. Traffic signals: | |
| (a) operation; | Partial – presence for vehicles and pedestrians recorded |
| (b) visibility. | Partial – recorded as part of intersection quality |
| 6. Objects, clear zones and road restraint systems: | |
| (a) roadside environment including vegetation; | ✔ |
| (b) roadside hazards and distance from carriageway or cycle path edge; | ✔ |
| (c) user-friendly adaptation of road restraint systems (central reservations and crash barriers to prevent hazards to vulnerable road users); | ✔ |
| (d) end treatments of crash barriers; | ✔ |
| (e) appropriate road restraint systems at bridges and culverts; | ✔ |
| (f) fences (in roads with restricted access). | ✔ |
| 7. Pavement: | |
| (a) pavement defects; | ✔ |
| (b) skid resistance; | ✔ |
| (c) loose material/gravel/stones; | ✔ |
| (d) ponding, water drainage. | ✔ |
| 8. Bridges and tunnels: | |
| (a) presence and number of bridges; | – |
| (b) presence and number of tunnels; | – |
| (c) visual elements representing hazards for the safety of the infrastructure. | ✔ |
| 9. Other issues: | |
| (a) provision of safe parking areas and rest areas; | – |
| (b) provision for heavy vehicles; | – |
| (c) headlight glare; | – |
| (d) roadworks; | ✔ |
| (e) unsafe roadside activities; | – |
| (f) appropriate information in ITS equipment (e.g. variable message signs); | – |
| (g) wildlife and animals; | – |
| (h) school zone warnings (if applicable).’; | ✔ |
Using proactive Star Ratings in conjunction with Road Safety Audits
RAP Star Ratings may be used in conjunction with Road Safety Audits to enhance safety outcomes. The Star Rating for Road Safety Audits (SR4RSA) manual provides practical examples for policy makers and practitioners. The following table summarises how Star Ratings align with the additional elements of Road Safety Audits listed in RISM Annex II.
| Indicative elements of road safety audits | Alignment with Star Rating methodology |
| (b) in section 1, the following point is added: | |
| ‘(n) provision for vulnerable road users: | |
| (i) provision for pedestrians; | ✔ |
| (ii) provision for cyclists, including the existence of alternative routes or separations from high-speed motor traffic; | ✔ |
| (iii) provision for powered two-wheelers; | ✔ |
| (iv) density and location of crossings for pedestrians and cyclists; | ✔ To 100m level |
| (v) provision for pedestrians and cyclists on affected roads in the area; | ✔ |
| (vi) separation of pedestrians and cyclists from high-speed motor traffic or the existence of direct alternative routes on lower class roads. | ✔ Existence of alternative routes requires additional assessments/review using Star Ratings and/or CycleRAP methodologies. |
| (c) in section 2, point (h) is replaced by the following: | |
| ‘(h) provision for vulnerable road users: | |
| (i) provision for pedestrians; | ✔ |
| (ii) provision for cyclists; | ✔ |
| (iii) provision for powered two-wheelers;’; | ✔ |