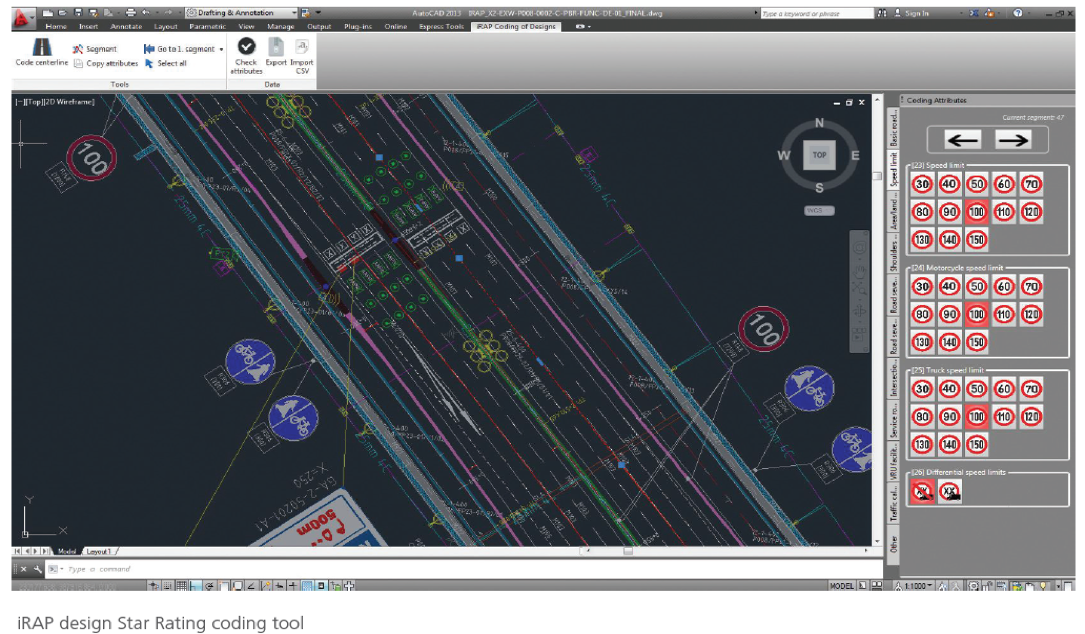
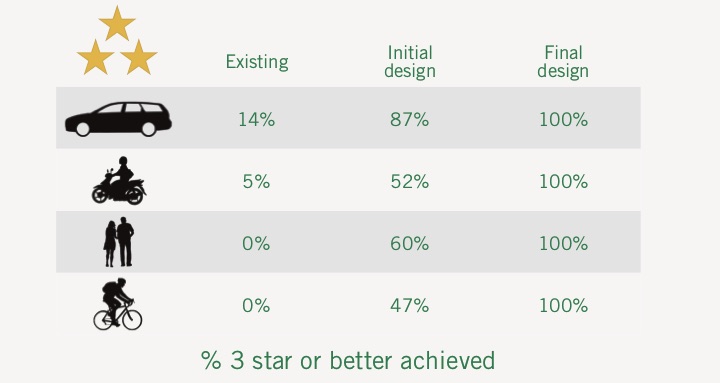
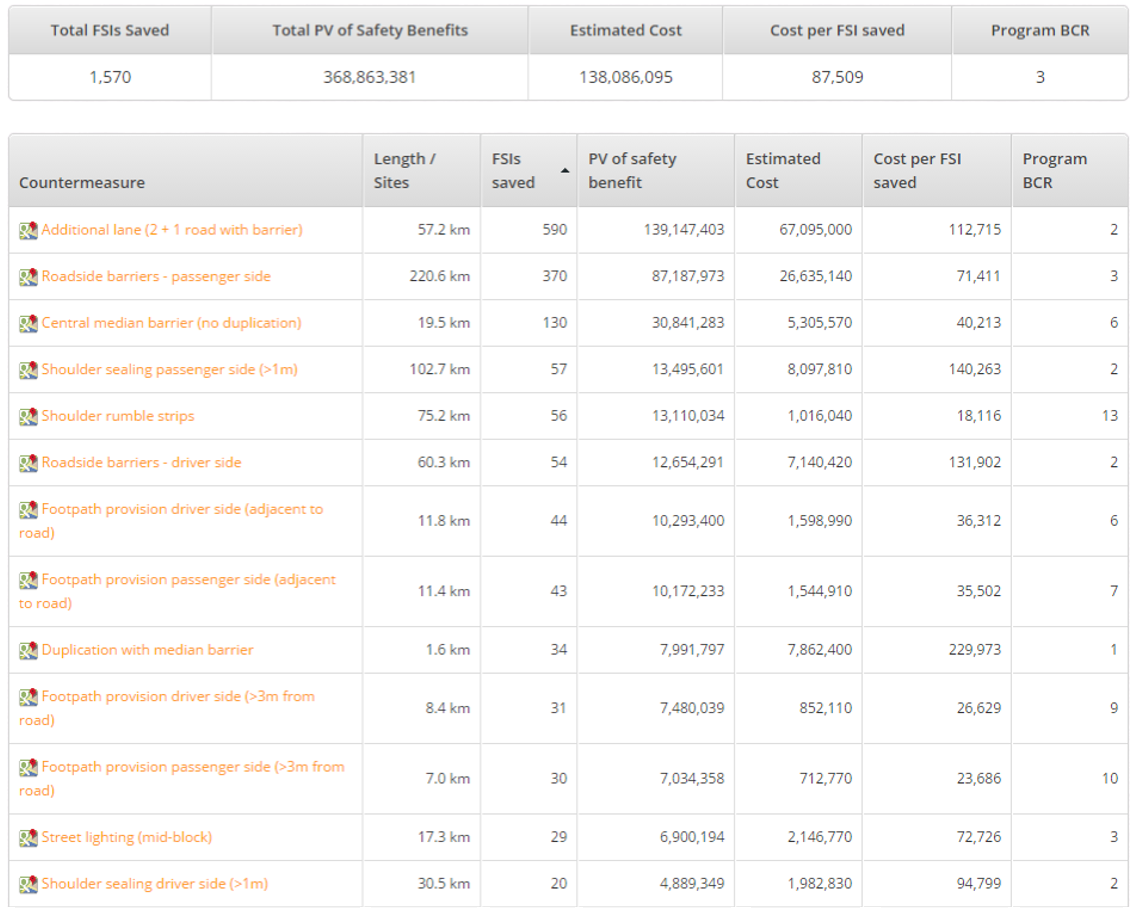
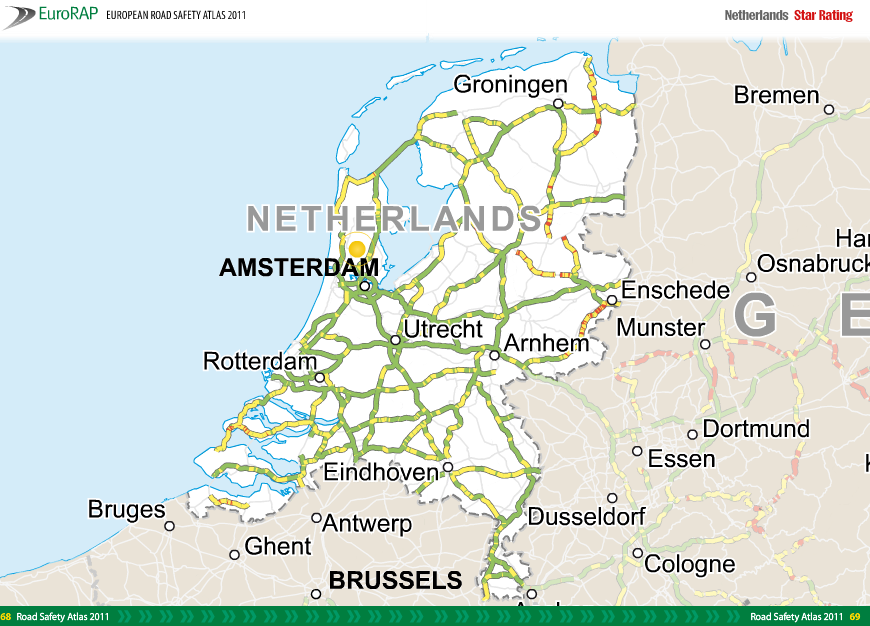
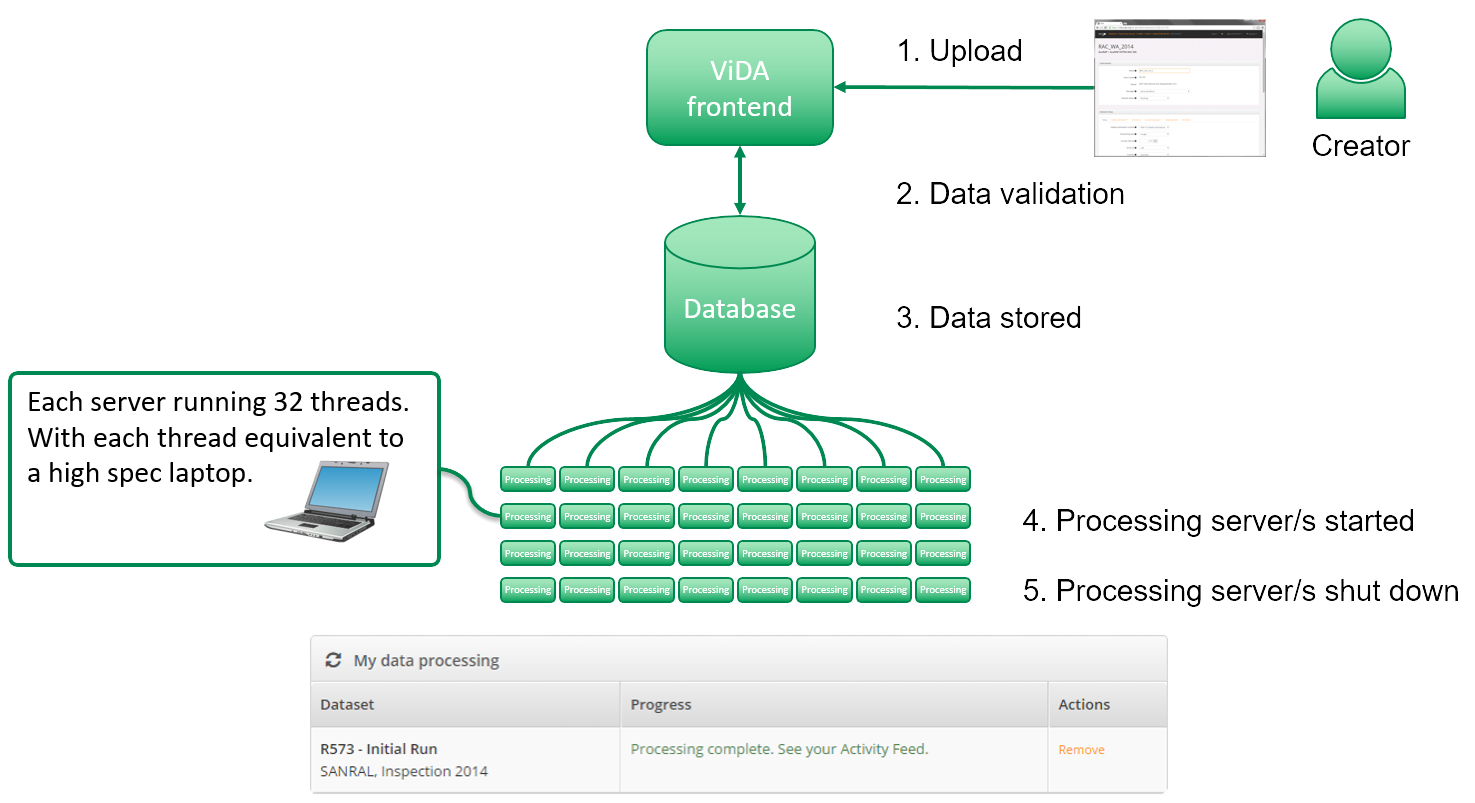
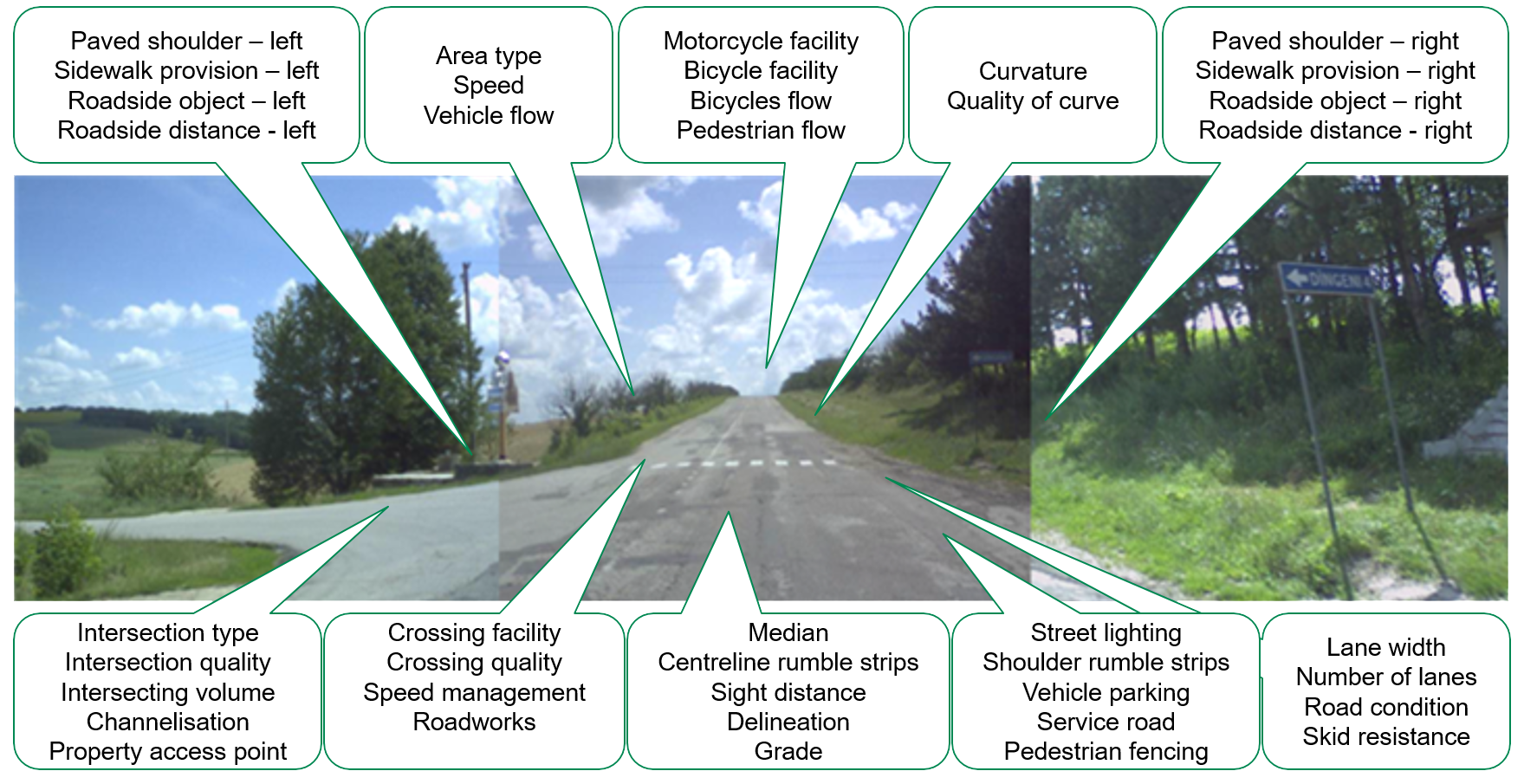
RAP Infrastructure Safety Management Tools
iRAP and its partners have developed a suite of tools that use the iRAP methodology to support infrastructure safety management globally and locally.
Tools developed with partners that use the iRAP methodology are known as RAP apps or Made Safer by iRAP apps. The iRAP methodology and related tools are overseen by the Global Technical Committee (GTC) and managed within the Innovation Framework.
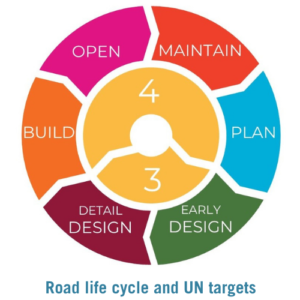
The tools support achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), the Global Plan for Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030 and Global Road Safety Performance Targets 3 and 4.
|
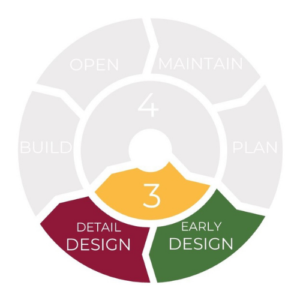
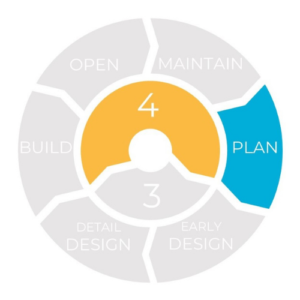
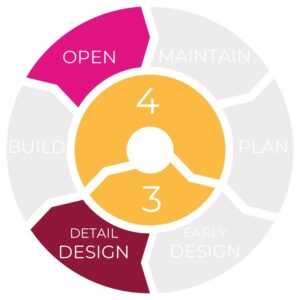
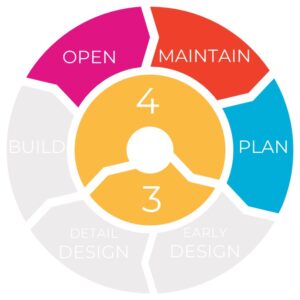
The tools can be used at all stages of a road’s lifecycle: – Planning: includes strategy, policy and project concepts.
|
|
The International Road Assessment Programme (iRAP) is a Registered Charity with UN ECOSOC Consultative Status.
iRAP is registered in England and Wales under company number 05476000
Charity number 1140357
Registered office: 60 Trafalgar Square, London, WC2N 5DS
GET IN TOUCH │ Europe │ Africa │ Asia Pacific │ Latin America and Caribbean │ North America