Nearly 1,500km of Nepal’s high-risk strategic road network has been assessed by The Department of Roads (DOR), supported by the World Bank and iRAP, to improve safety conditions and guide future works planning and investment.
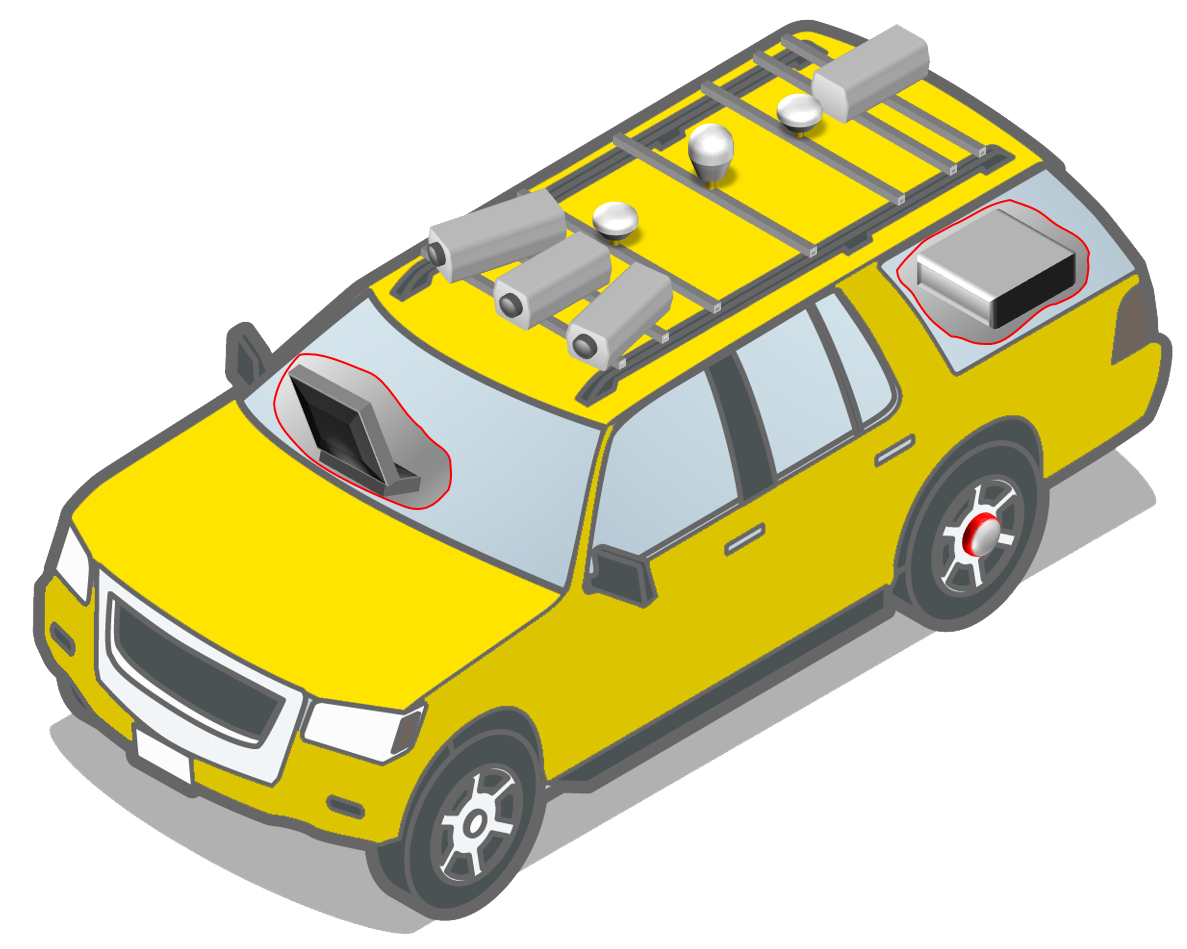
Using its own resources and consultant for video surveillance, high-risk road sections have been identified by DOR, helping to optimize targeted investment to improve safety.
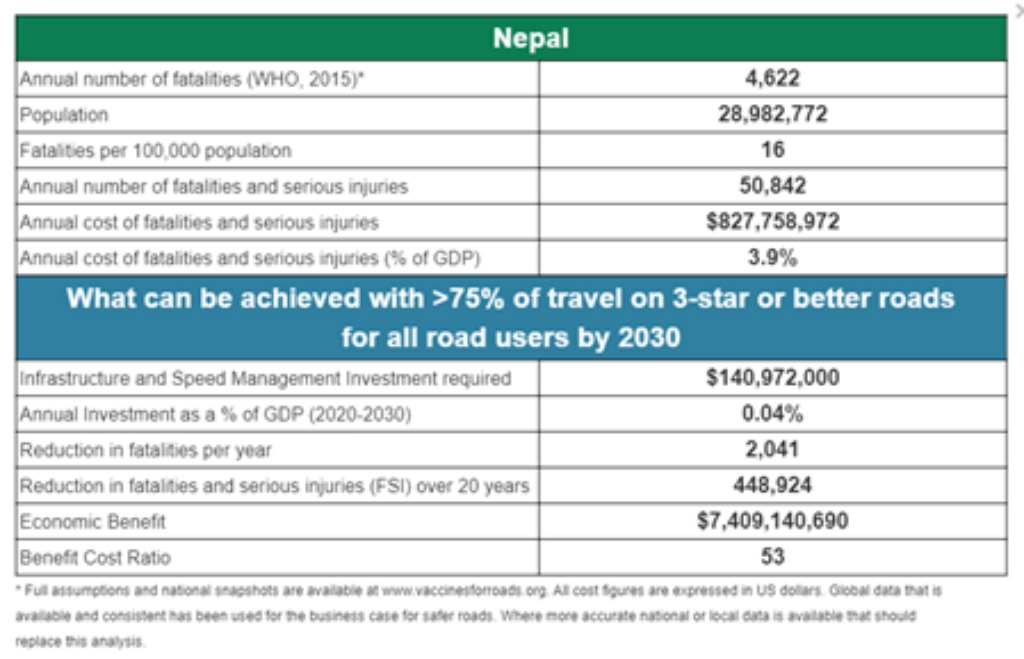
According to World Health Organisation 2015 data, more than 4,600 people die on Nepal’s roads annually. Fatalities and serious injuries cost the country’s economy more than USD$827 million each year.
The baseline Star Ratings of the 1,457km of existing roads showed that 41% of the assessed road length is rated 3-star or better for vehicle occupants, 32% for motorcyclists,14% for pedestrians and 36% for bicyclists.
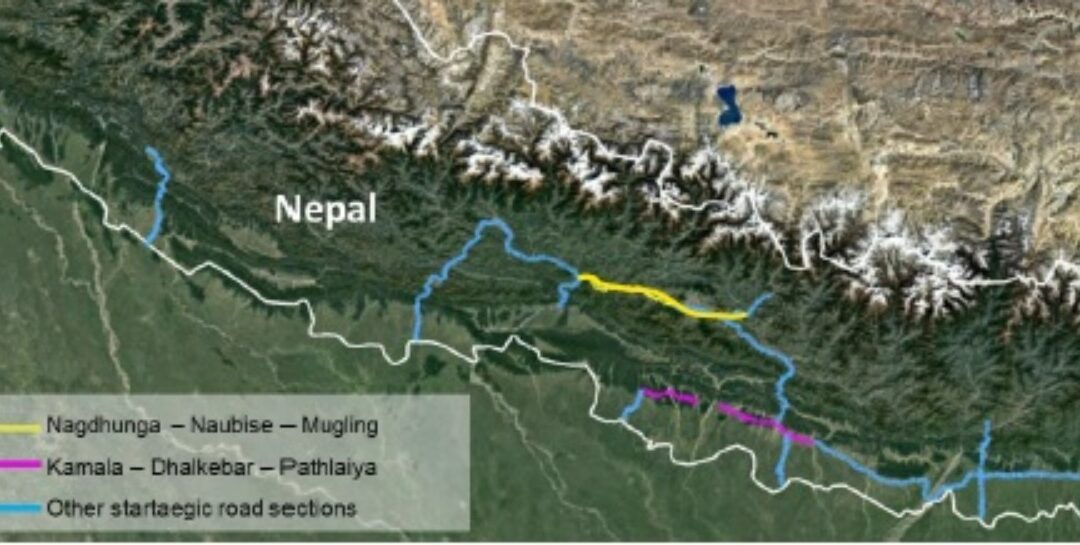
The assessment included two road sections identified for improvement under World Bank’s Safe Corridor Demonstration Programme: Nagdhunga to Mugling (via Naubise) and Kamala to Pathlaiya (via Dhalkebar), west and south of Kathmandu respectively.
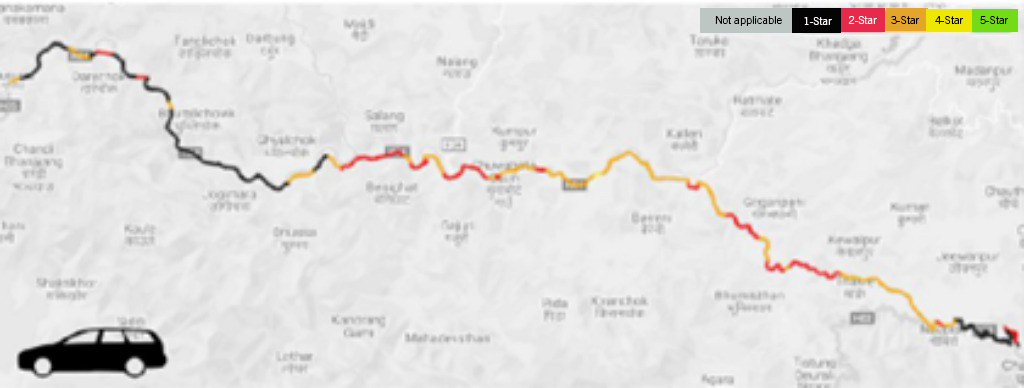
Nagdhunga – Naubise – Mugling section
The Star Rating results for the Nagdhunga – Naubise – Mugling section (95 km) indicate that: 41% of the assessed road length is rated 3-star or better for vehicle occupants, 28% for motorcyclists,18% for pedestrians and 22% for bicyclists.
Star Rating results for Vehicle Occupants: Nagdhunga to Mugling via Naubise
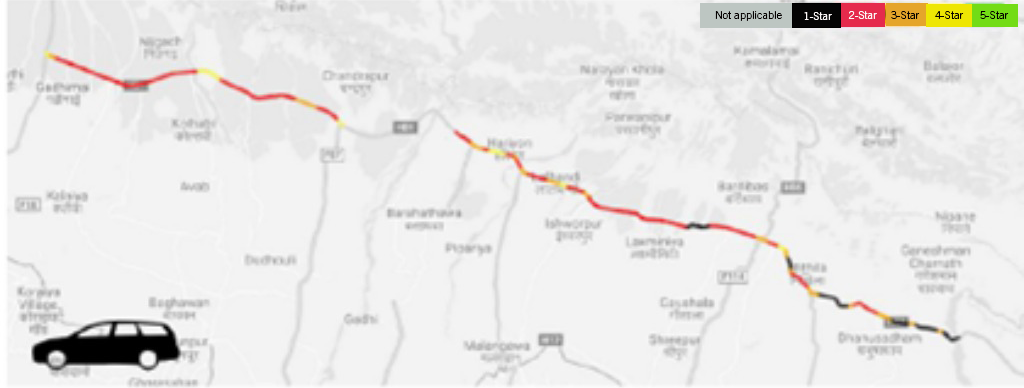
Kamala – Dhalkebar – Pathlaiya section
The Star Rating results for the Kamala – Dhalkebar – Pathlaiya section (114.5 km) indicate that: 26% of the assessed road length is rated 3-star or better for vehicle occupants, 23% for motorcyclists,2% for pedestrians and 13% for bicyclists.
Star Rating results for Vehicle Occupants: Kamala to Pathlaiya (via Dhalkebar)
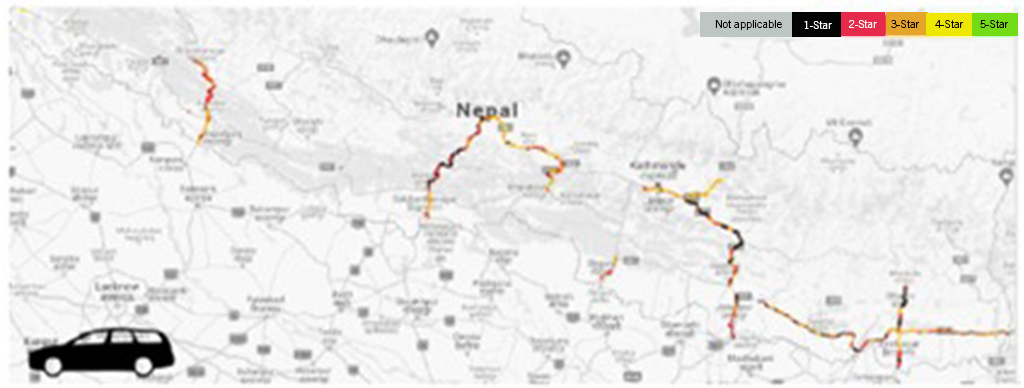
Remaining other strategic road sections
The Star Rating results for the remaining other strategic road sections (1,246.9 km) indicate that: 42% of the assessed road length is rated 3-star or better for vehicle occupants, 33% for motorcyclists,14% for pedestrians and 39% for bicyclists.
Star Rating results for Vehicle Occupants: Remaining road sections
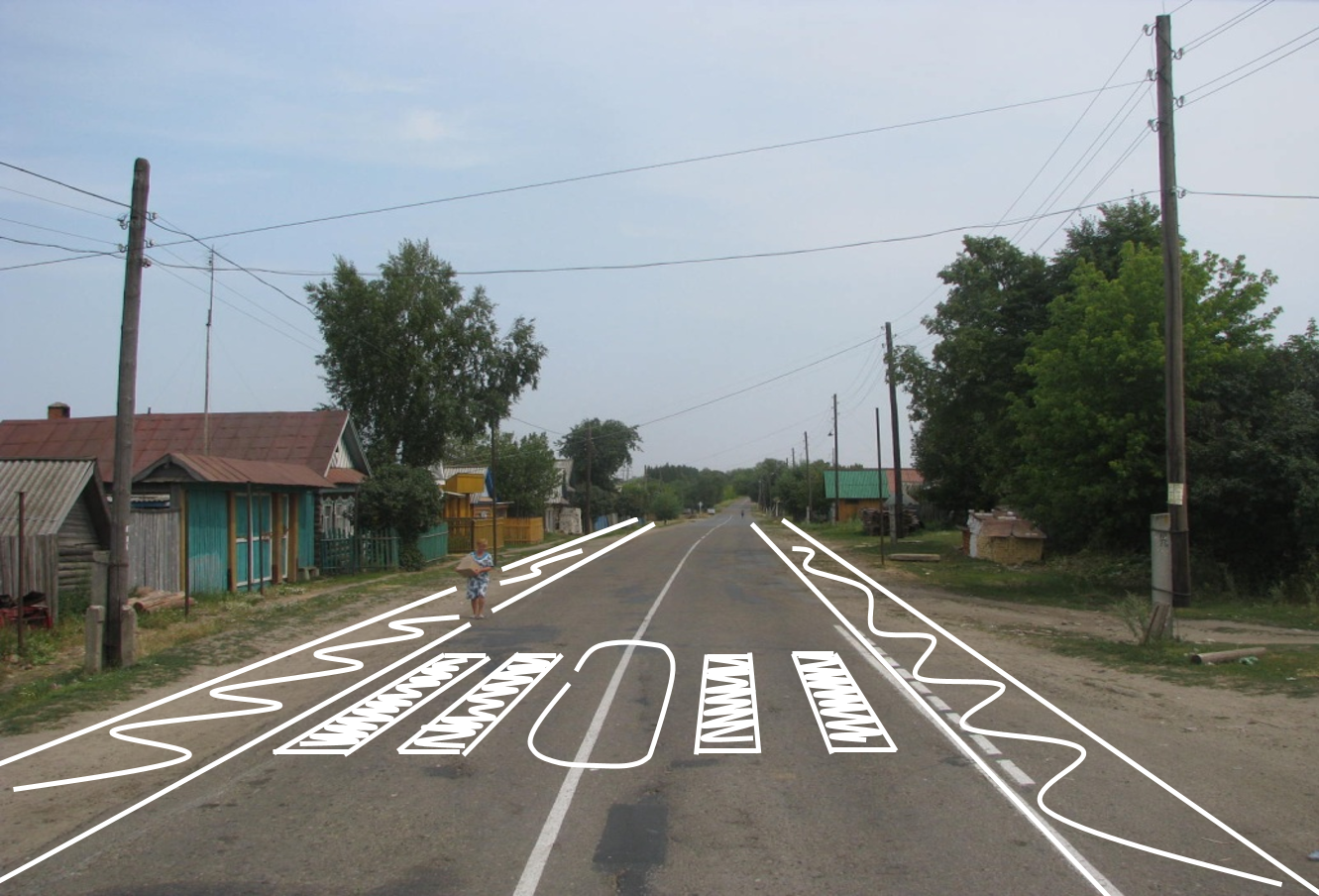
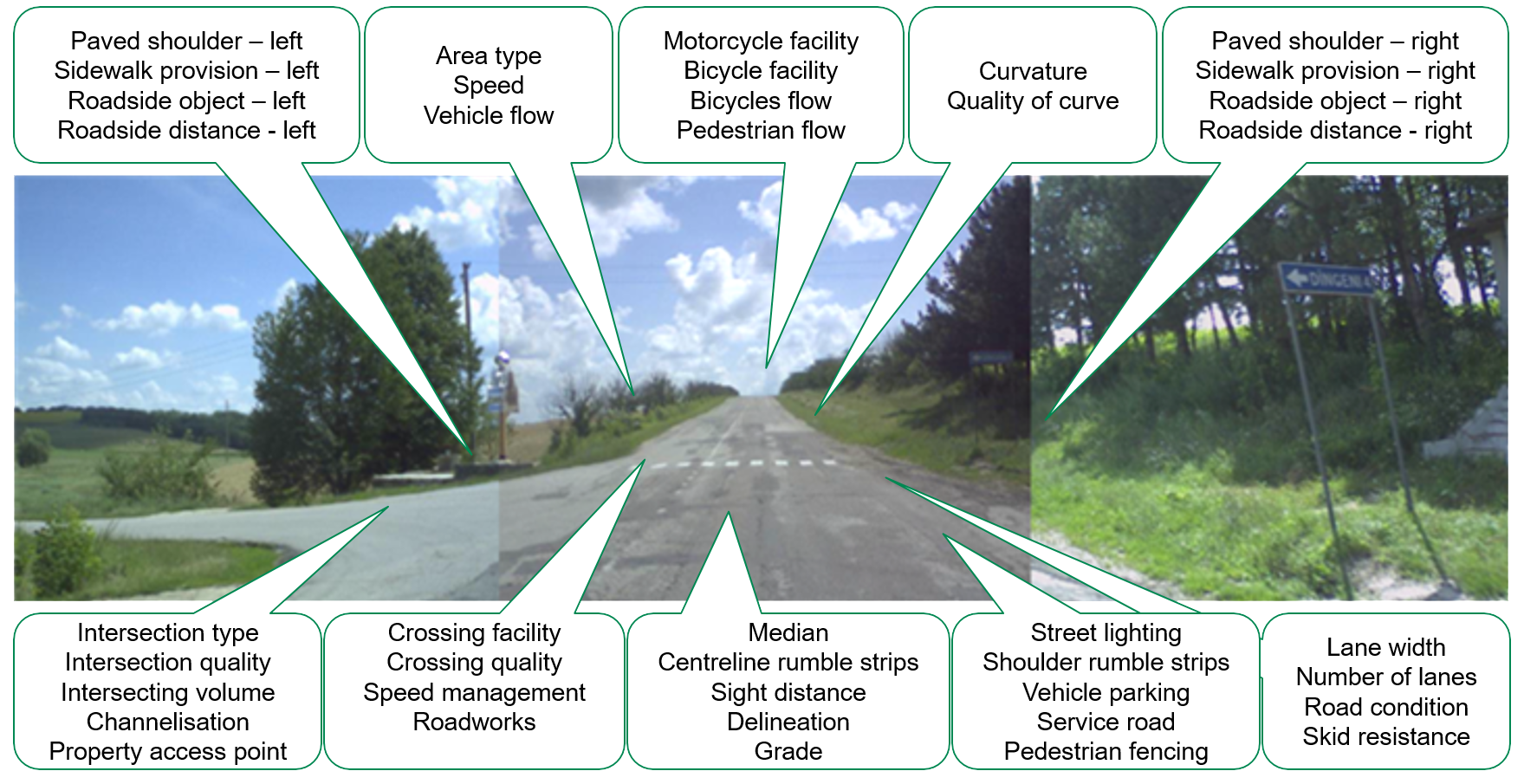
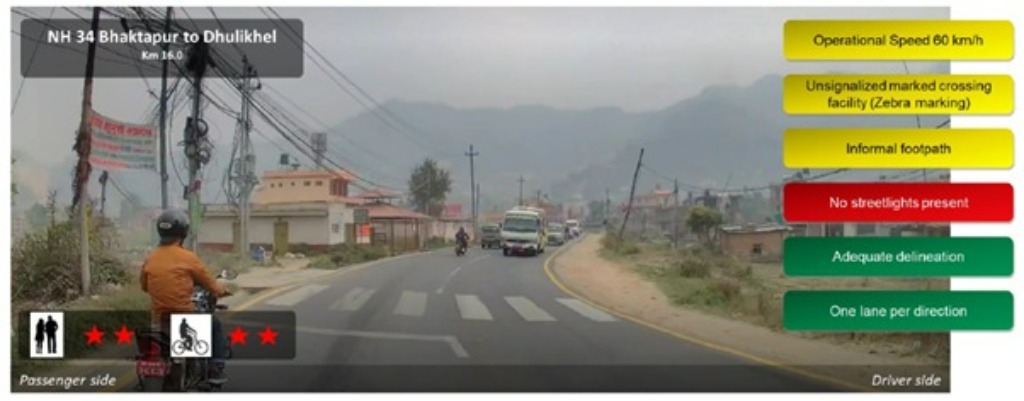
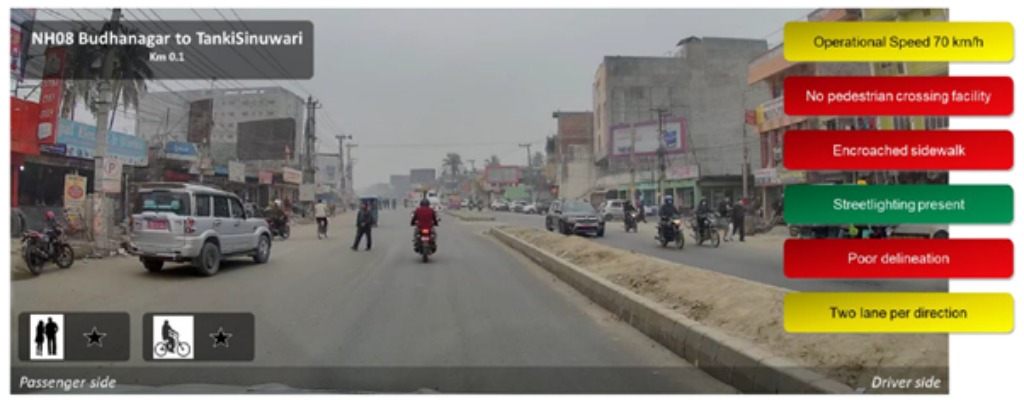
Example Star Rating images from the assessed network
The level of risk associated with a network infrastructure, and hence its Star Rating, is a function of numerous attributes, including travel speeds. This is demonstrated in the following assessment images:




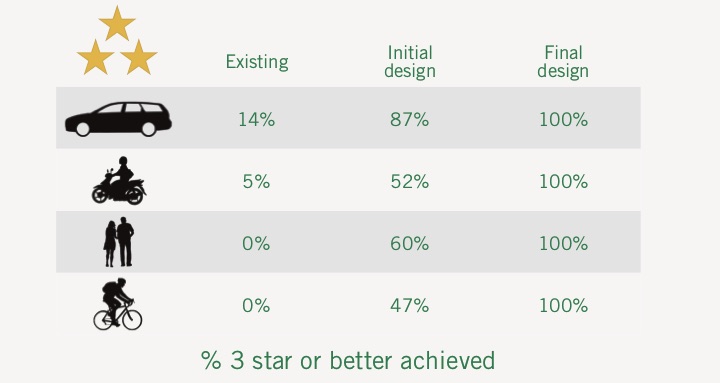
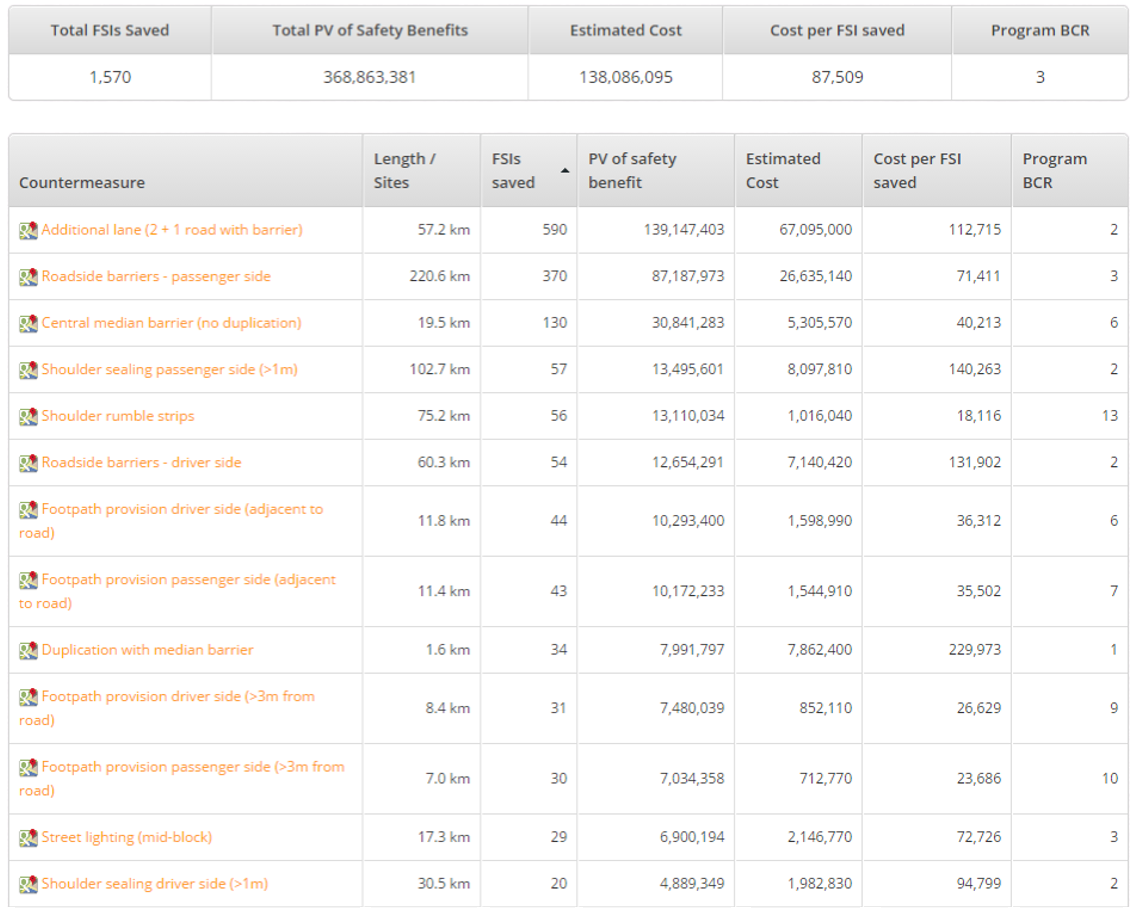
Safer Roads Investment Plans prepared as part of the project have identified infrastructure solutions to improve the Star Ratings, reduce the frequency and severity of road crashes, and prevent deaths and serious injuries.
Recommended countermeasures include the provision of roadside safety barriers and footpaths, road duplication or addition of lanes with median barrier, delineation and intersection improvements and installation of traffic calming measures.
Three potential investment plans have been prepared for consideration with the most comprehensive showing that by investing NPR 25.4 billion (USD$200 million), the number of fatalities and serious injuries on the assessed strategic road network could be reduced by up to 60%, saving around 57,734 fatalities and serious injuries over 20 years. The overall benefit to cost ratio would be $3 of benefit for every $1 spent.
DOR is now seeking to have its staff accredited in this process. iRAP training for DOR staff has commenced and an additional 500km pilot project will be undertaken to build local capacity in managing and undertaking systematic road safety assessments using the iRAP methodology.
The Safe Corridor Demonstration Project will also be delivered including a feasibility study of the treatments identified and preparation of road designs evaluated for safety prior to construction using Star Rating for Designs.
Ensuring the provision of safe facilities for pedestrians, cyclists, and other non-motorized modes in Nepal’s cities and towns will enable growth in active transport modes and the achievement of related environmental and public health goals.
The Department of Roads is responsible for incorporating adequate safety measures during the construction and maintenance of about 13,000 km of Strategic Road Network which serves as the backbone for the physical and economic integration of the country.
Under the Ministry of Physical Infrastructure and Transport (MoPIT), the DOR is also responsible for planning, construction, project management and maintenance of the National highways, Feeder roads and strategically important urban roads.
iRAP and local partners have undertaken a number of assessments since 2014 and an estimated USD$682.44 million of road investment has been made safer informed by iRAP assessments.
Nepal is undergoing a historic transition toward a federal and secular republic. This represents a window of opportunity for the country to further reduce poverty, increase the income of the bottom 40%, and pursue its ambitious agenda of inclusive growth and accountable service delivery.*
According to the iRAP Vaccines for Roads Big Data Tool, achieving >75% of travel on 3-star or better roads for all road users in Nepal by 2030 stands to save 2,041 fatalities a year with an economic benefit of USD$7.4 billion.
* Source: https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/nepal