Young people bear the brunt of the road safety tragedies.
Road crashes are the leading cause of death for youth, claiming the lives of more than 186,300 children annually (WHO, 2015).
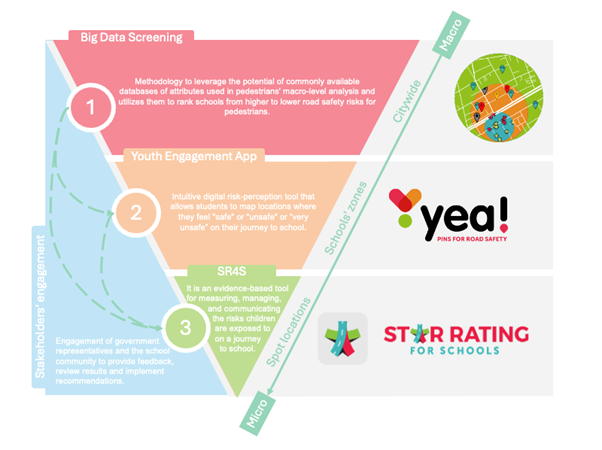
iRAP proposed a framework to ensure safe travels to school.
The Tools
Big Data Screening Methodology:
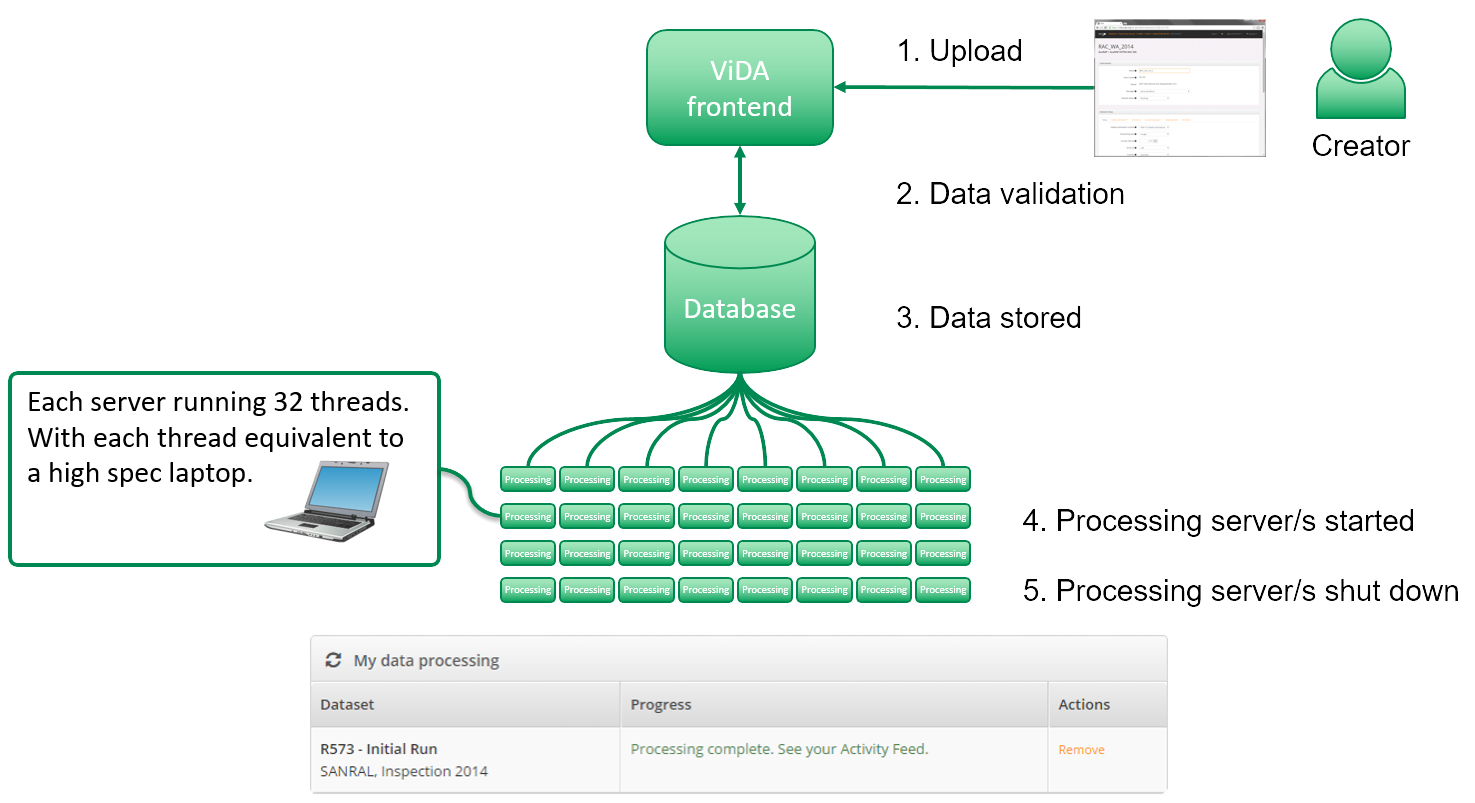
The Methodology was developed by iRAP in collaboration with the AIP Foundation and Anditi. It was conceived to harness existing data sources, whether open-source or secured through purchase agreements. Its primary objective is to optimize data collection, ensuring access to relevant information while minimizing costs. The method uses commonly available attributes in pedestrians’ macro-level analysis and utilizes them to rank schools from higher to lower road safety risks for pedestrians.
The attributes are then categorized into four different analytical levels, where the method reduces the amount of data collected as the level progresses. At each level, the schools are ranked, and only the high-risk ones will progress to the following analysis stage. The Methodology is documented in the report Big Data Analysis: Methodology for assessing high-risk schools.
Youth Engagement App:

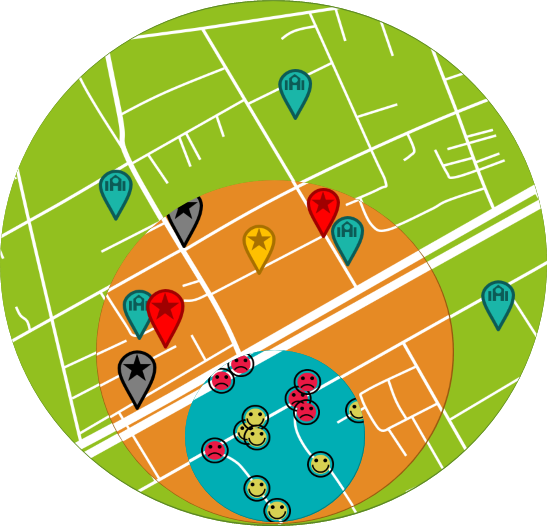
All pedestrian assessment pins reported by students on YEA are directly integrated into the SR4S platform to help identify areas with high concentrations of pin clusters and prioritize those points for detailed assessment of infrastructure through SR4S. Functioning as a versatile data collection tool and more, the YEA serves as a guiding platform for sharing valuable insights regarding youth perceptions of the road environment.
YEA is available for use, and data is open for visualization. To use the App in your projects or to access to the data, please contact the Project team.
More information is available in the YEA website.


Star Rating for Schools:
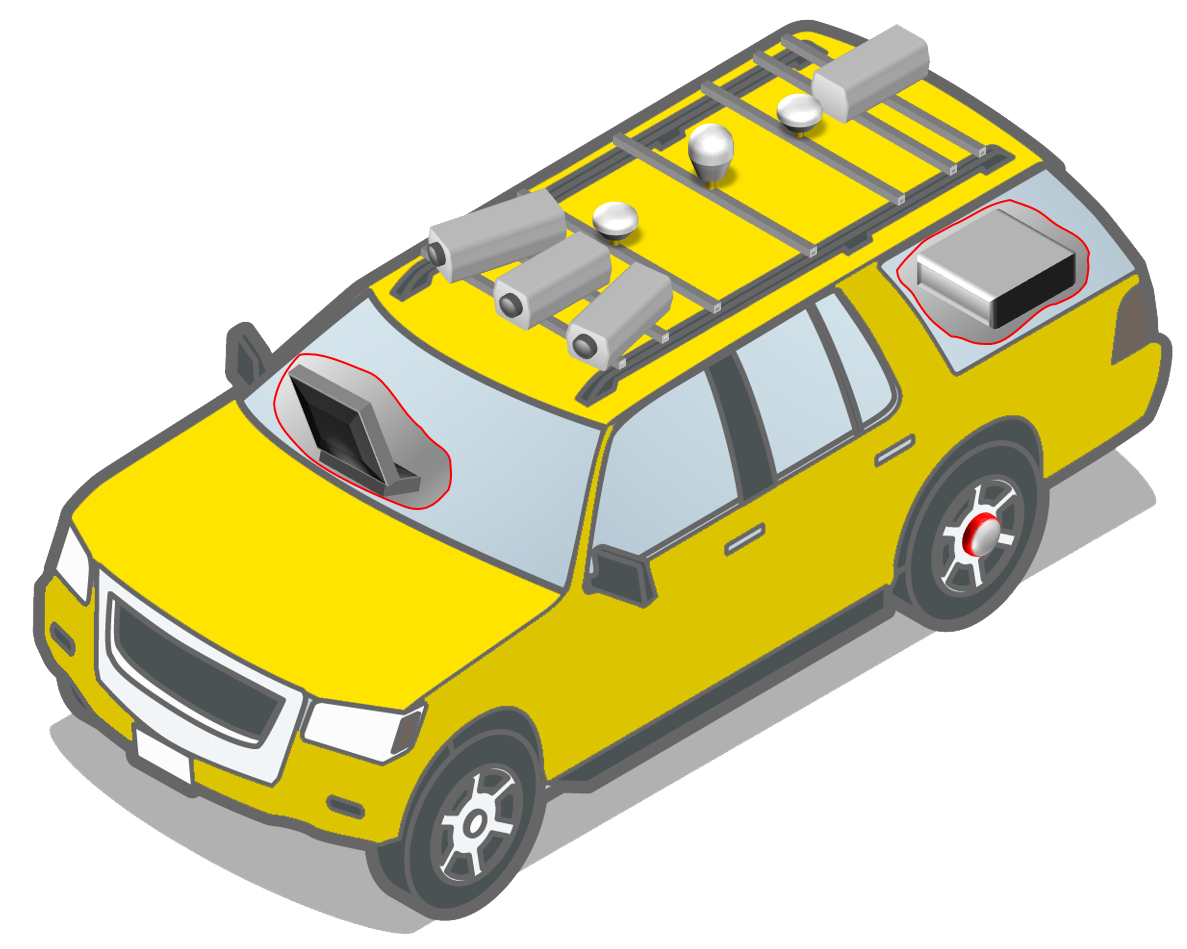
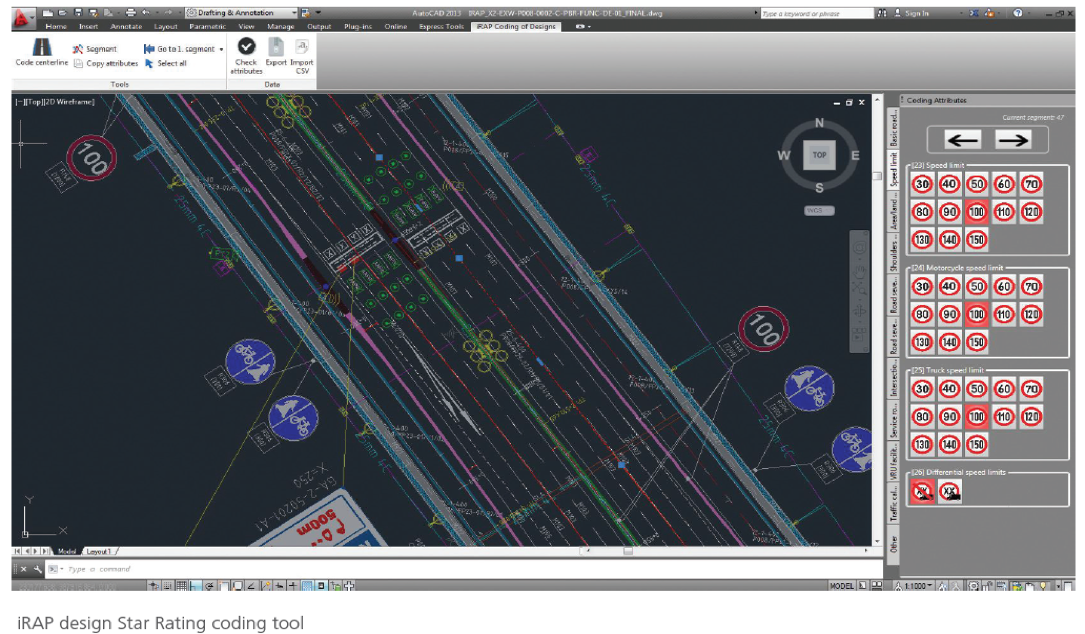
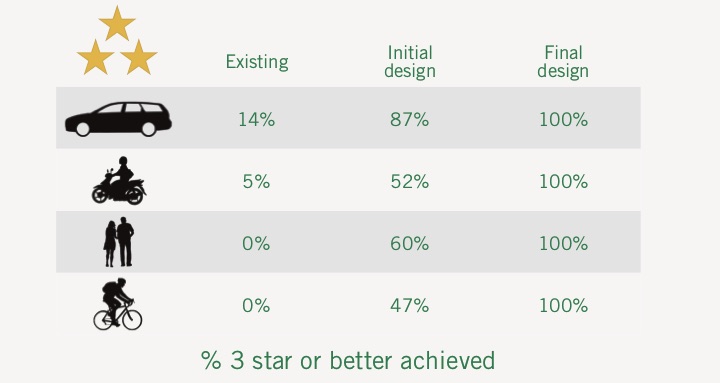
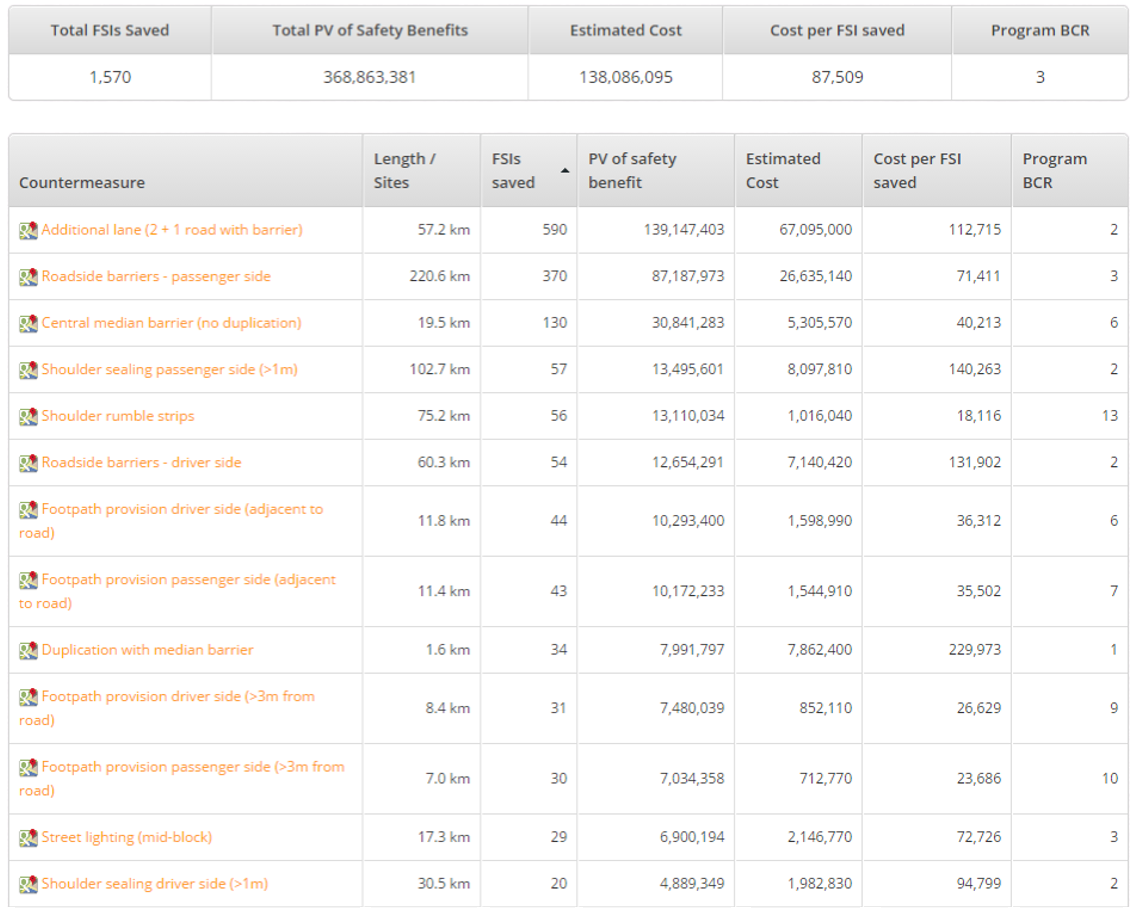
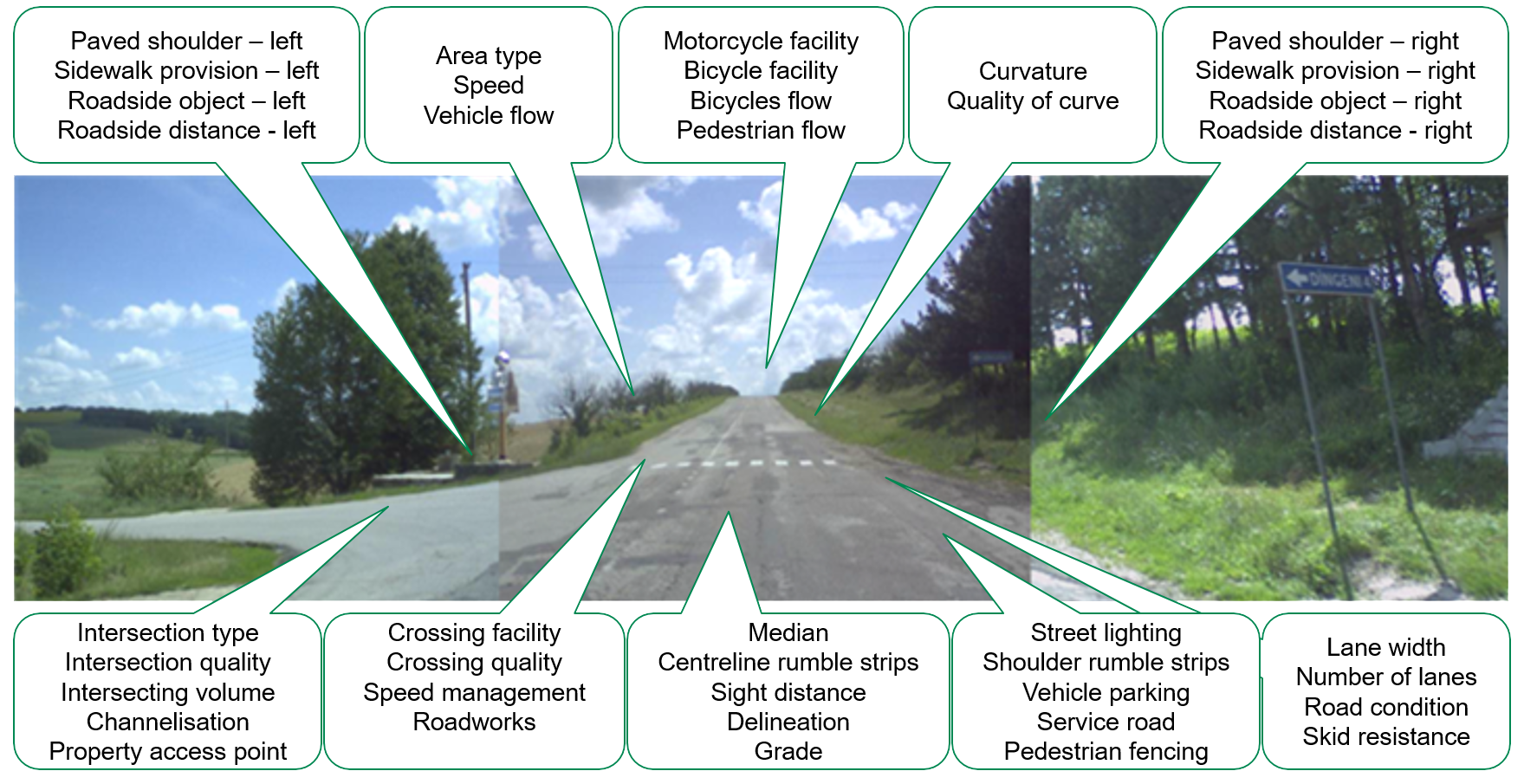
The list of high-risk schools screened using the Big Data method, combined with data reported by YEA users, underwent an in-depth assessment of infrastructure safety using the SR4S assessment tools to produce upgrade recommendations. Star rating results, where five stars are the safest and 1 star is the least safe are generated at each site. Schools with a low star rating of 1 or 2 stars are given priority by the government in the renovation plan. More information about SR4S is available on the program website. At the heart of SR4S lies a meticulous system for data collection using the iRAP global standard. Trained coders follow standardized guidelines to gather data on various attributes systematically. This systematic and quality-assured approach forms the foundation for calculating road safety risks, ensuring a thorough and accurate assessment.
To know more about the SR4S access visit starratingforschools.org