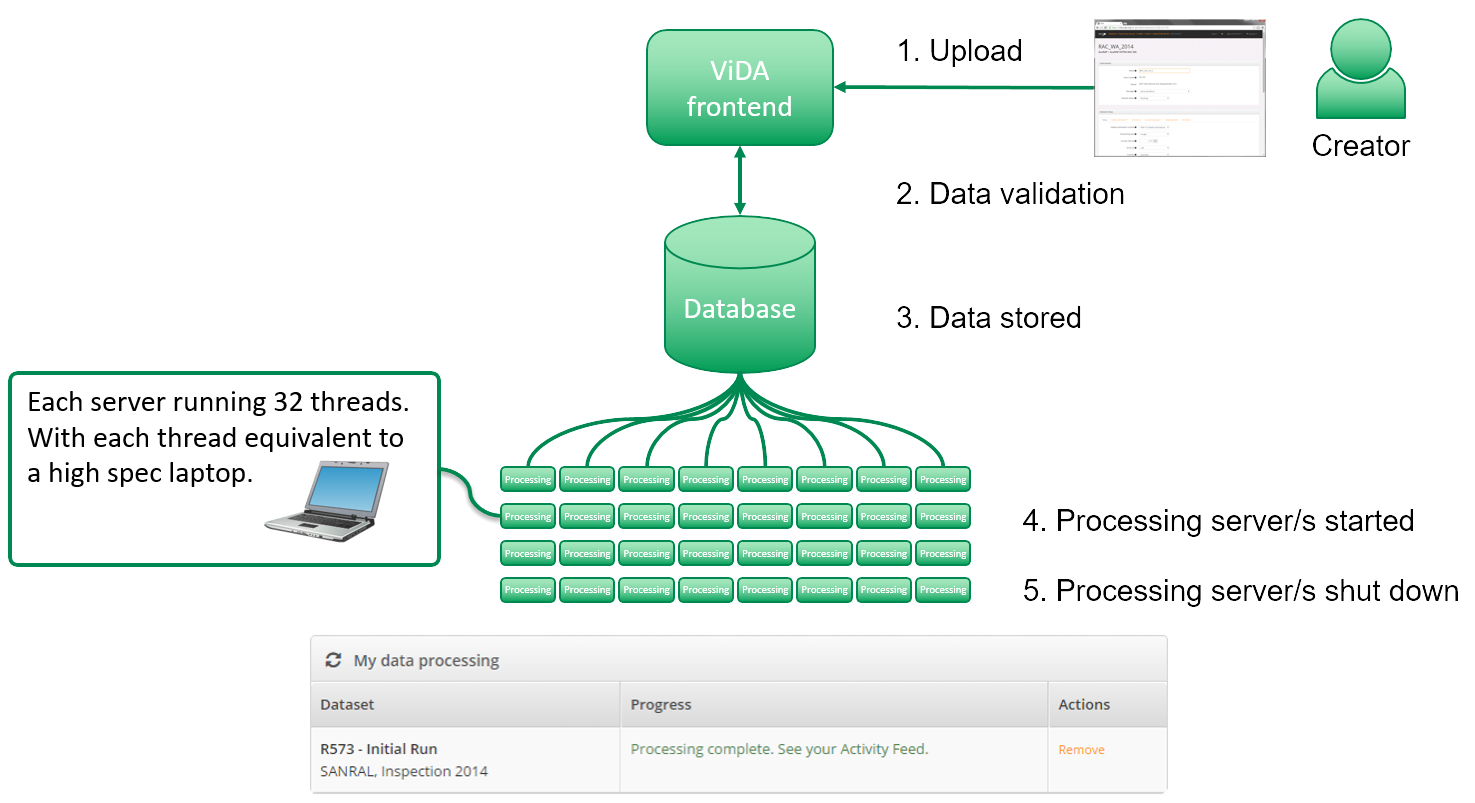
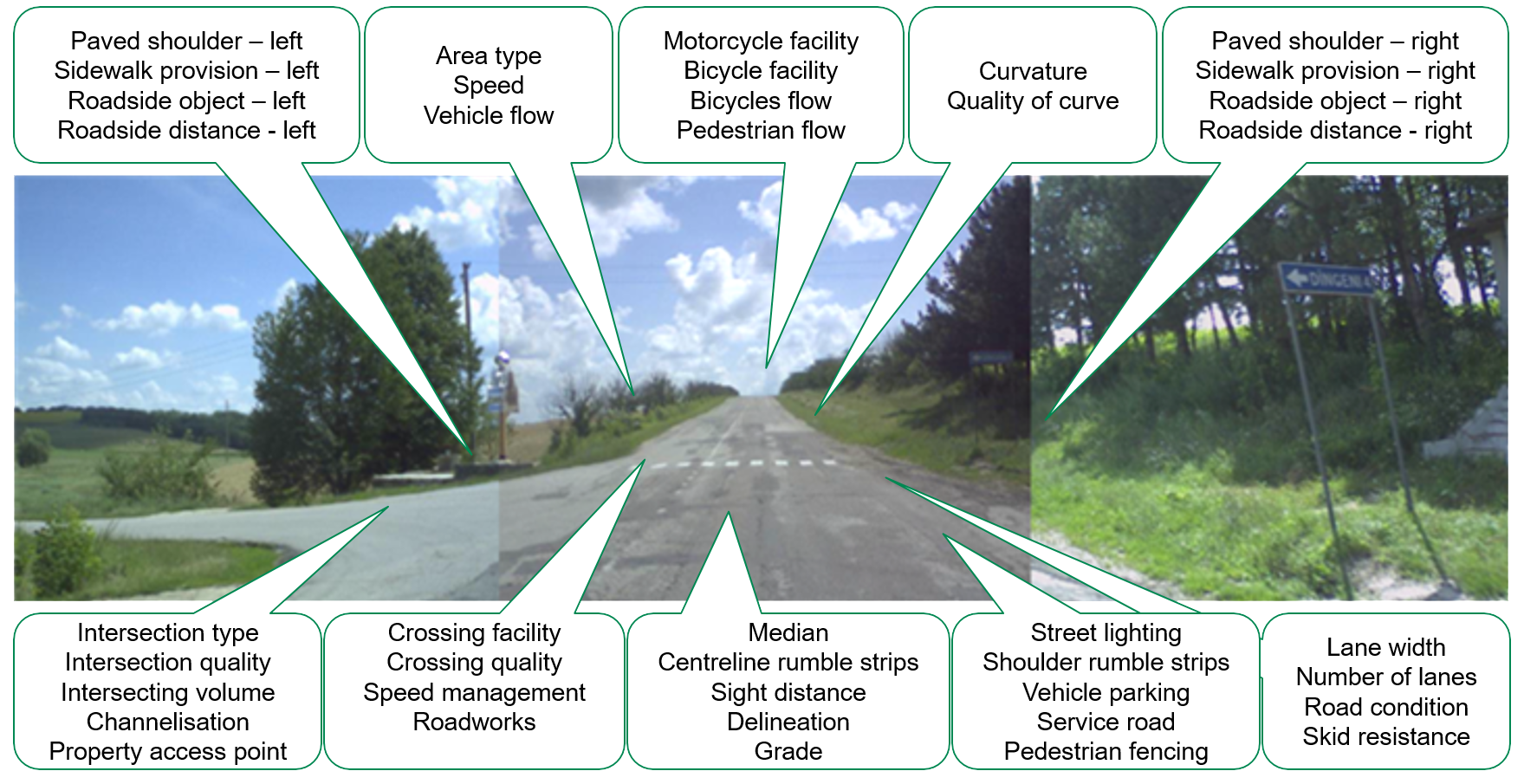
Description
Decimal Star Ratings offer a more sensitive, nuanced, and actionable way to understand and communicate road safety. Whether you’re evaluating infrastructure improvements, analysing safety scenarios, or tracking progress along a road corridor, decimal ratings give you that extra layer of insight beyond whole-star thresholds.
Decimal Star Ratings are an enhancement of the traditional 1- to 5-star rating system used by iRAP to express road safety risk. Traditional Star Ratings assign a whole‑number rating (1‑5) based on a Star Rating Score (SRS), which reflects the relative risk of death or serious injury for road users—through vehicle, motorcycle, cyclist, and pedestrian metrics—using a model based on road attributes.
Decimal Star Ratings add granularity within each star band by subdividing each whole‑star band into tenths. This finer representation allows you to see where exactly within the band the score falls—e.g., 3.5 indicates the middle of the 3‑star band, while 3.9 is near the top.
What are Decimal Star Ratings?
Enhanced resolution: Whole‑star jumps can be broad. The decimal ratings helps highlight even small safety improvements, which might not otherwise result in a full star increase but still represent meaningful progress.
Better decision support: In tools like iRAP’s Star Rating Demonstrator and Route Review Tool (RRT), decimal ratings enable clearer evaluation of incremental improvements—useful in scenario testing or network‑level assessments.
Route-level insight: For longer routes, the Route Decimal Star Rating is typically a flow-weighted average over all assessed segments. This helps engineers prioritise those sections where the largest impacts of improvements would be.
Status
Decimal Star Ratings are implemented in tools like the Star Rating Demonstrator (ViDA platform), replacing the former Star Rating Score display with decimal values. Decimal Star Ratings will be fully implemented in early 2027.