In an innovative approach to combat urban heat, Blacktown City Council in Australia has leveraged AiRAP artificial intelligence to strategically identify the maximum number of locations for new shade-producing roadside tree plantings without detrimentally impacting road safety.
Whilst preserving the road network’s safety Star Ratings, this proactive initiative aims to reduce carbon emissions and improve the health of residents, addressing multiple pressing challenges the council faces, including a disturbing rate of diabetes – currently double the national average.
Urban heat is a significant issue in Blacktown, where the population experiences heat bank problems that are among the highest in the Sydney region. Coupled with a predominantly immobile populace and 40% higher energy usage than adjacent suburbs, this project emerges as a critical component in the city’s environmental strategy.
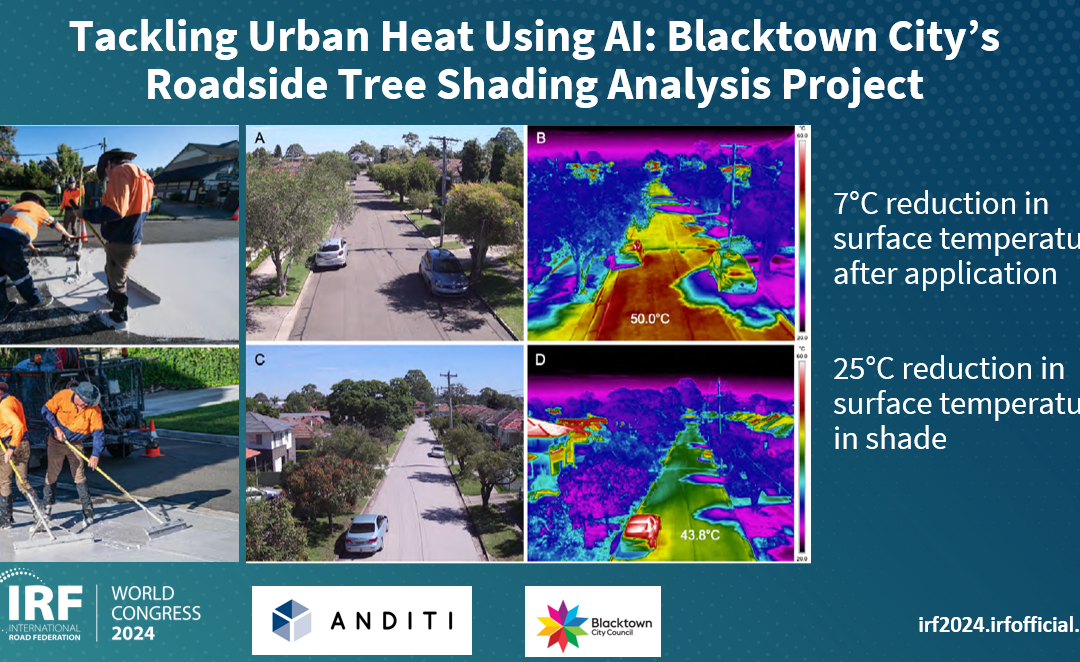
To support its Roadside Tree Shading Analysis Project, Blacktown City Council engaged Anditi to undertake a successful pilot study along a 3 km stretch of Palmyra Avenue.
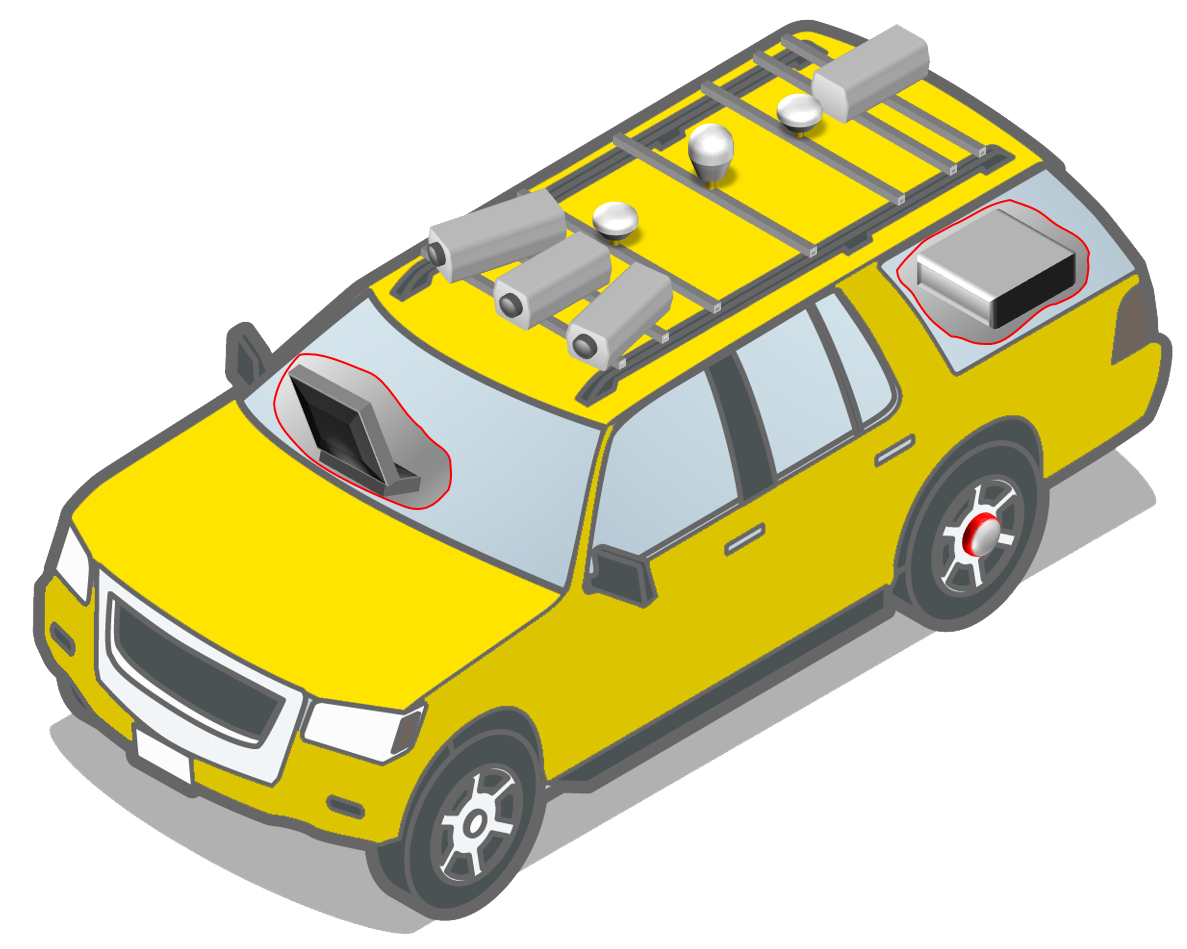
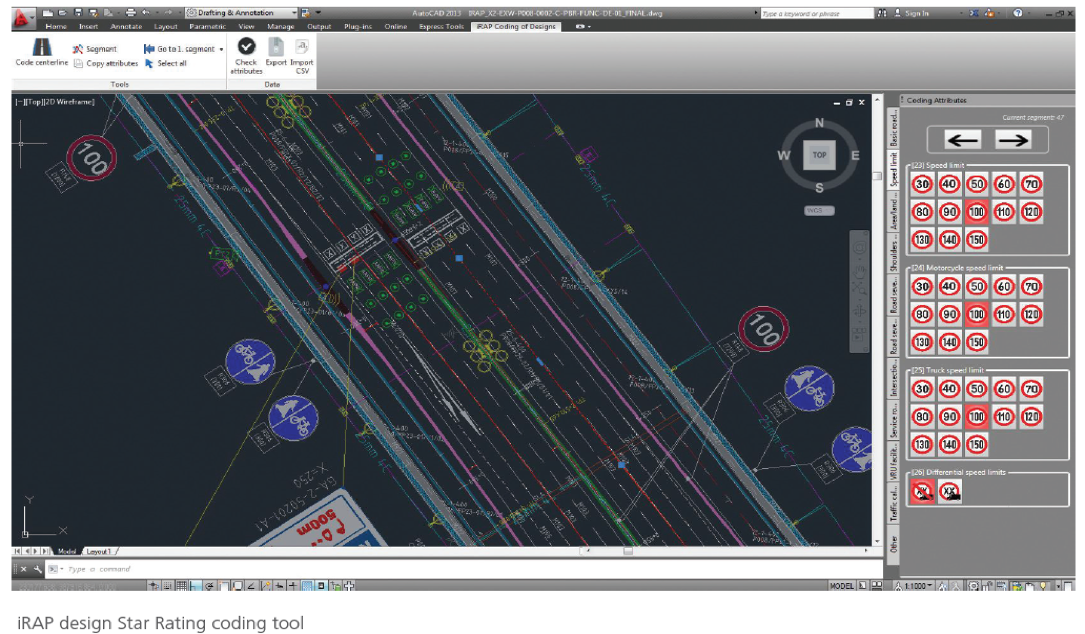
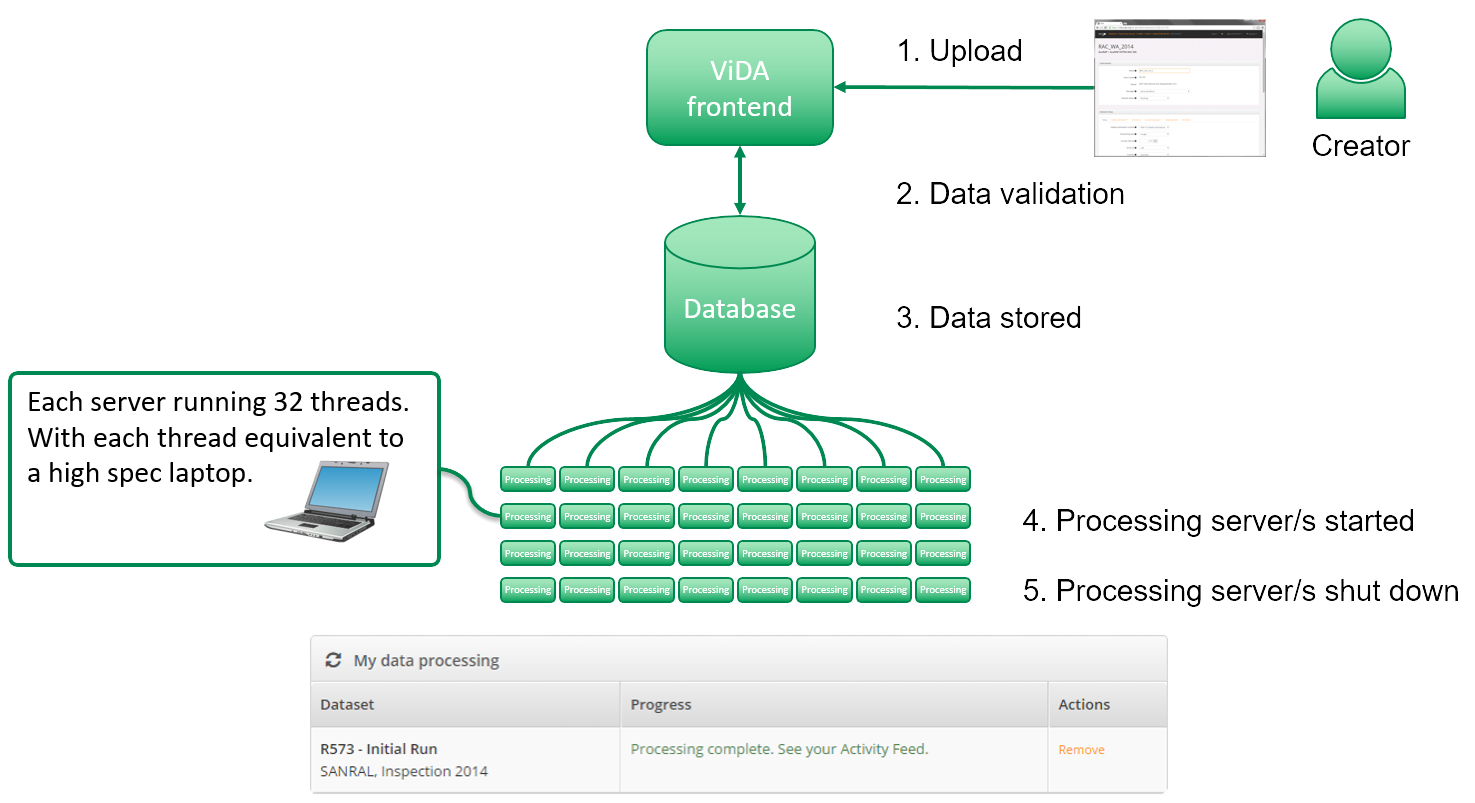
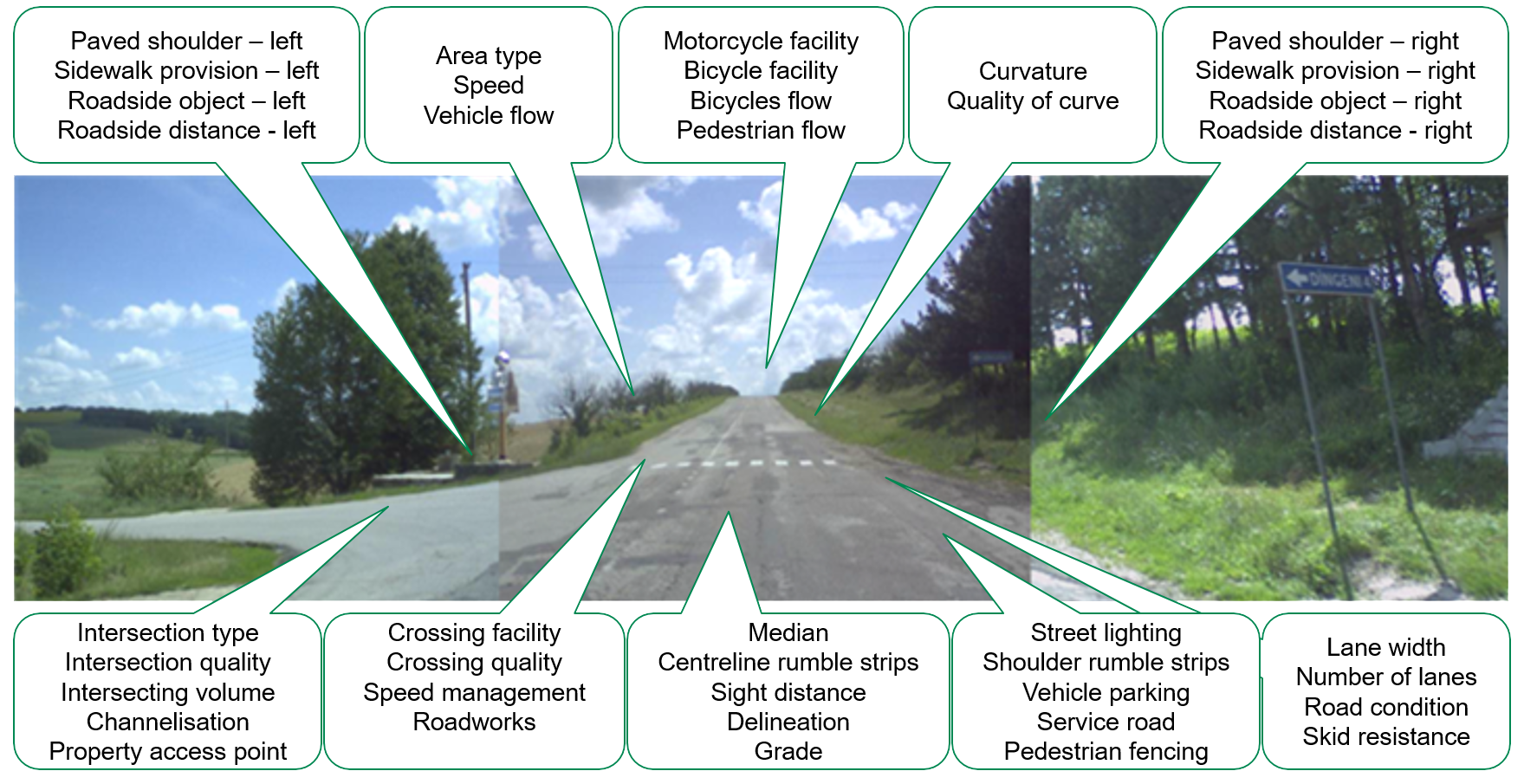
Utilizing advanced mobile LiDAR technology, an iRAP road safety assessment was undertaken, existing shading was calculated, and new potential trees were virtually integrated into the model, allowing accurate predictions of the shading and Star Ratings impacts.

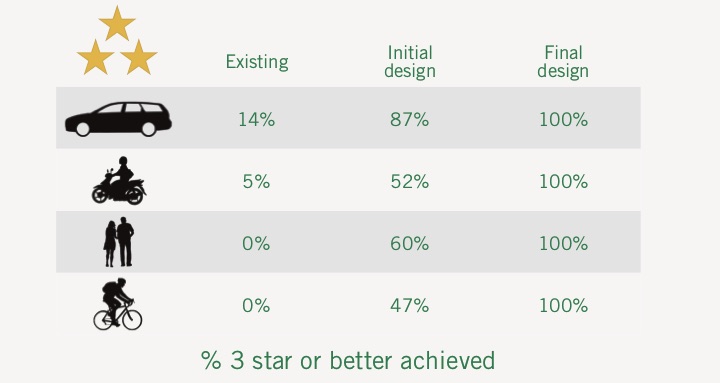
By employing a robust analysis of the existing road network and collaborating closely with the Council’s landscape team, the project identified optimal locations for planting new trees, whilst ensuring the introduction of greenery would not disrupt road safety.
Key outcomes of the project include:
- Significant Surface Temperature Reduction: Initial findings indicated a remarkable average reduction in surface temperature of 7°C after the application of modeled trees, with shaded areas seeing a decrease of up to 25°C.
- Road Safety Assurance: Collaboratively conducted safety assessments utilized the AusRAP and AiRAP Star Rating methods, ensuring that road safety remains a top priority.
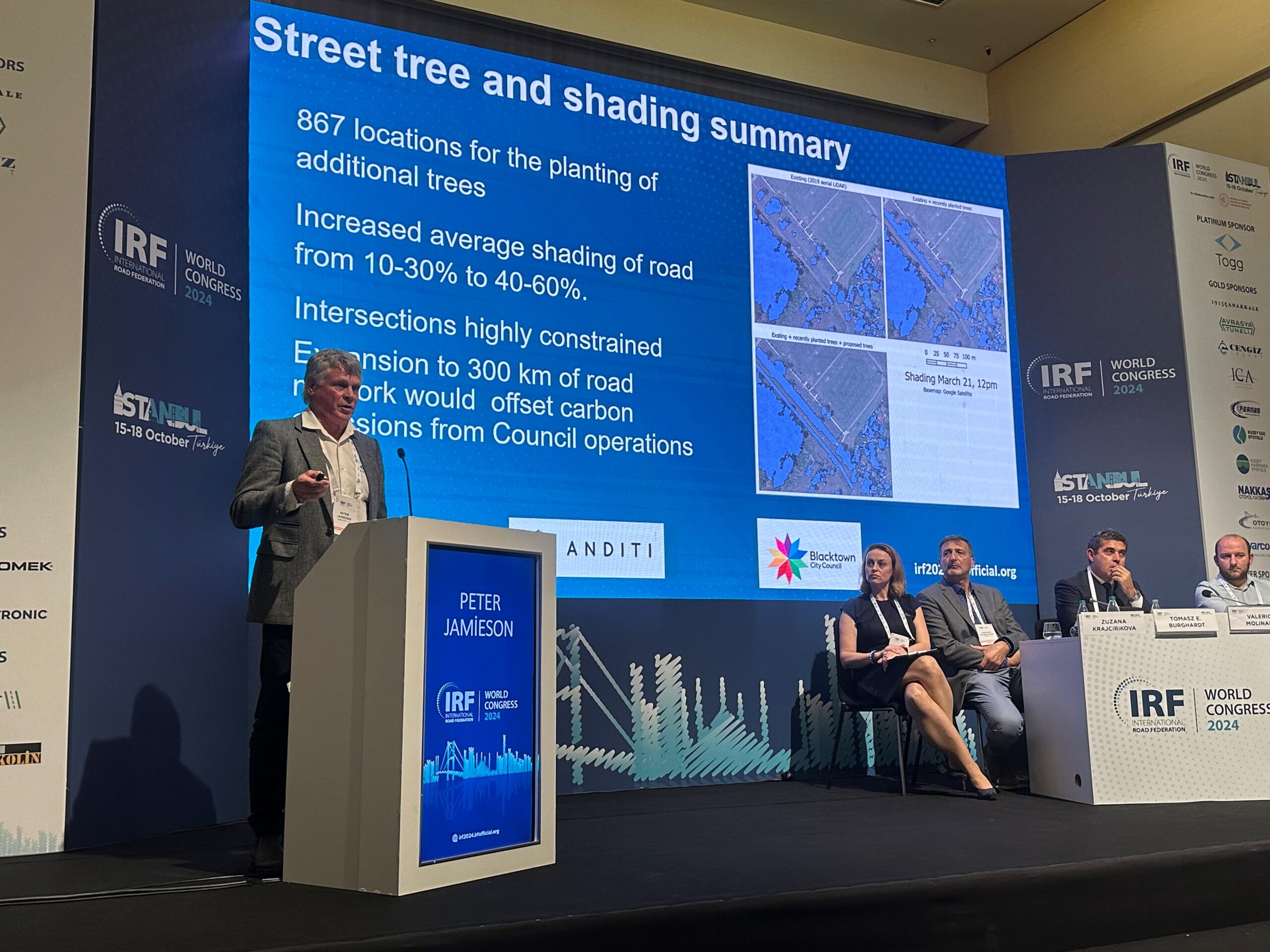
- Enhanced Urban Greening: The project outlined 770 potential planting locations, comprising 33 large trees, 67 medium trees, and 670 small trees. These additional trees promise to increase road shading from an existing 10-30% to a targeted 40-60%.
- Carbon Neutrality Potential: If the trees are planted along the entire 300 km road corridor, the operation of the Council would become carbon neutral, showcasing the project’s far-reaching impact on reducing the overall carbon footprint.
- Health and Lifestyle Improvements: In tackling the alarming diabetes prevalence in Blacktown—currently at 8 people per 100, the second highest in Sydney —the initiative aims not only to cool the area but also to promote physical activity by creating more pleasant outdoor environments.
The project is a brilliant example of cross-council collaboration between Blacktown, Parramatta and Campbelltown Councils, employing the latest AiRAP innovation of Anditi, for a united effort to enhance community well-being and protect the environment.
As it embarks on this transformational journey, Blacktown City Council anticipates that the Roadside Tree Shading Analysis Project will serve as a repeatable and scalable model for future urban greening initiatives, fostering a healthier, cooler, and more resilient community.
Anditi Managing Director Peter Jamieson presented the project and its findings on the global stage at the IRF World Congress in Istanbul yesterday.